Transcriptomic and metabolomic insights into the synergistic effects of resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid on hepatic function under varying protein diets in Tibetan sheep
- PMID: 40697554
- PMCID: PMC12279703
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1614114
Transcriptomic and metabolomic insights into the synergistic effects of resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid on hepatic function under varying protein diets in Tibetan sheep
Abstract
Background: Increasing evidence indicated resveratrol (RES) and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid (HMB) regulated several biological processes via modulating gene expression. This study employed transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses to investigate the impact of RES and HMB supplementation, in combination with varying dietary protein levels on hepatic immunity, antioxidant capacity, and morphology in Tibetan sheep.
Methods: Two treatments (with or without RES and HMB supplementation) and two dietary protein levels (12% vs. 14% of the basal diet) were tested according to a 2 × 2 factorial arrangement within a Latin square design. A total of 120 healthy two-month-old male Tibetan lambs (16.87 ± 0.31 kg) were randomly allocated for 90-day feeding experiment, with the following treatments: low-protein basal diet without (L group) or with (L-RES + HMB group) supplemental 1.50 g/d RES and 1.25 g/d HMB, and high-protein basal diet without (H group) or with (H-RES + HMB group) supplemental 1.50 g/d RES and 1.25 g/d HMB.
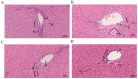
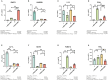
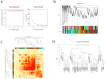
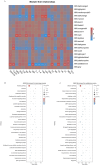
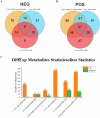
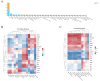
Results: The results indicated that the liver tissue structure was predominantly normal in the H-RES + HMB group, devoid of central vein congestion. The catalase (CAT) activity and total antioxidant (T-AOC) capacity were significantly increased when fed the 14% protein diet (p < 0.05). The superoxide dismutase (SOD) and CAT activities of sheep fed supplementary-treated diets were significantly increased than the basal diet (p < 0.05). Immunoglobulin M (IgM) level and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) activity in the H-RES + HMB group were significantly increased than those in the H and L groups (p < 0.05), whereas interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) levels were significantly lower (p < 0.05). A total of 4,236 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified, including 3,503 upregulated genes and 733 downregulated genes, which were categorized into immune-related KEGG signaling pathways. Metabolomic analysis identified that compared to L group, the abundance of 918 metabolites were significantly changed in H-RES + HMB group including 829 upregulated and 89 downregulated. Those differential metabolites enriched in KEGG pathways primarily related to immunity and antioxidation.
Conclusion: Dietary protein level and RES/HMB supplementation exhibited positively interaction effect on immunity and antioxidant capacity. The 14% protein diet with RES and HMB improved the hepatic function through modulating the gene and metabolite in Tibetan sheep.
Keywords: Tibetan sheep; liver; metabolome; resveratrol; transcriptome; β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhu, Zhang, Wu, Hou and Gui.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Exploring the effects of resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid under different protein levels on the ileal health of tibetan sheep.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 21;16:1612170. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612170. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40761281 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of resveratrol and β-Hydroxy-β-methyl butyric acid supplementation alone or in combination on the development and health of the duodenum in Tibetan sheep.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jul 8;16:1612102. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1612102. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40698187 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and lipid metabolome of the subcutaneous fat of Tibetan sheep: A comprehensive analysis of the reduction in fat deposition upon resveratrol and β-hydroxy-β-methyl butyric acid supplementation.Genomics. 2025 Jul 7;117(5):111078. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2025.111078. Online ahead of print. Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40633702
-
Effects of β-hydroxy β-methylbutyrate (HMB) supplementation on muscle mass, function, and other outcomes in patients with cancer: a systematic review.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022 Jun;13(3):1623-1641. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.12952. Epub 2022 Mar 17. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2022. PMID: 35301826 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Yang G, Tao L, Xiong Z, Lin W, Teng L, Zhang X. Resveratrol mitigates oxidative stress and suppresses HBV replication via modulation of the SIRT1-Nrf2 pathway in liver cells. Future Virol. (2025) 20:83–92. doi: 10.1080/17460794.2025.2478750 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

