Predicting hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Insights from a nomogram model
- PMID: 40697588
- PMCID: PMC12278073
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.107501
Predicting hypertension in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Insights from a nomogram model
Abstract
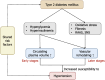
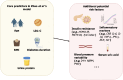
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is rising, with hypertension as a common comorbidity that significantly increases cardiovascular and microvascular risks. Accurate prediction of hypertension in T2DM is essential for early intervention and personalized management. In this editorial, we comment on a recent retrospective study by Zhao et al, which developed a nomogram model using a large cohort of 26850 patients to predict hypertension risk in patients with T2DM. The model incorporated key independent risk factors, including age, body mass index, duration of diabetes, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and urine protein levels, demonstrating promising discriminative power and predictive accuracy in internal validation. However, its external applicability requires further confirmation. This editorial discusses the clinical value and limitations of the predictive model, highlighting the unfavorable impact of hypertension on T2DM patients. Future research should evaluate the potential contribution of other risk factors to enhance risk prediction and improve the management of T2DM comorbidities.
Keywords: Blood pressure variability; Diabetes; Hypertension; Inflammatory markers; Insulin resistance; Nomogram model; Risk prediction; Serum uric acid; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Preexisting Diabetes and Pregnancy: An Endocrine Society and European Society of Endocrinology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline.Eur J Endocrinol. 2025 Jun 30;193(1):G1-G48. doi: 10.1093/ejendo/lvaf116. Eur J Endocrinol. 2025. PMID: 40652450
-
[Association between obesity and the risk of microvascular complications in Yinzhou District, Ningbo adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus].Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2025 Jul;54(4):608-620. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2025.04.012. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40695761 Chinese.
-
The comparative and added prognostic value of biomarkers to the Revised Cardiac Risk Index for preoperative prediction of major adverse cardiac events and all-cause mortality in patients who undergo noncardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Dec 21;12(12):CD013139. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013139.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34931303 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of serum uric acid and homocysteine levels in predicting the occurrence of atrial fibrillation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Biomed Eng Online. 2025 Jul 9;24(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s12938-025-01418-0. Biomed Eng Online. 2025. PMID: 40634998 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, Stein C, Basit A, Chan JCN, Mbanya JC, Pavkov ME, Ramachandaran A, Wild SH, James S, Herman WH, Zhang P, Bommer C, Kuo S, Boyko EJ, Magliano DJ. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hu Y, Wang Z, He H, Pan L, Tu J, Shan G. Prevalence and patterns of multimorbidity in China during 2002-2022: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ageing Res Rev. 2024;93:102165. - PubMed
-
- Ji Q, Chai S, Zhang R, Li J, Zheng Y, Rajpathak S. Prevalence and co-prevalence of comorbidities among Chinese adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional, multicenter, retrospective, observational study based on 3B study database. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2024;15:1362433. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

