Efficacy of Xiaokeqing granules and lifestyle intervention in treating prediabetes mellitus considering metabolomic biomarkers: A randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 40697595
- PMCID: PMC12278099
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v16.i7.105219
Efficacy of Xiaokeqing granules and lifestyle intervention in treating prediabetes mellitus considering metabolomic biomarkers: A randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Prediabetes mellitus (PDM) is receiving increasing attention as a precursor to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lifestyle and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) interventions are effective for PDM prevention and treatment. Therefore, we conducted a preliminary investigation and an exploratory randomised controlled trial to assess the effects of a combined lifestyle and TCM intervention on PDM indicators.
Aim: To study the effectiveness of Xiaokeqing granules (XQG) and lifestyle interventions in PDM participants while using metabolomics to identify potential markers.
Methods: Forty PDM participants with yin deficiency syndrome with excessive heat were recruited and randomly allocated to the control (Con) group or the XQG group (20 per group). The Con group underwent lifestyle interventions, whereas the XQG group underwent lifestyle and XQG interventions. The follow-up duration was 2 months. Fasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial glucose (2hPG), glycated haemoglobin A1c, fasting insulin, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance levels, and serum metabolomics characteristics were compared via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis.
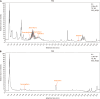
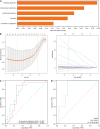
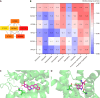
Results: There were significant differences in 2hPG between the two groups (P < 0.05) in the intention-to-treat analysis and per-protocol analysis. The intervention method used in this study was safe (P > 0.05). Groenlandicine, kaempferol, isomangiferin, etc., are the XQG constituents absorbed in the blood. N-Nervonoyl methionine and 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan are core potential metabolomic biomarkers for the effectiveness of XQG and lifestyle interventions. HTR1A, HTR2C, SLC6A4, etc., are the core targets of XQG and lifestyle interventions, as well as the reason for their clinical efficacy. Possible mechanistic pathways include tryptophan metabolism, pantothenate and certificate of analysis biosynthesis, lysine degradation and biosynthesis of cofactors.
Conclusion: This pilot study provides evidence that a combined XQG and lifestyle intervention can improve 2hPG in participants with PDM. The mechanism of action is related to multiple constituents, targets and pathways.
Keywords: Lifestyle; Metabolomics; Prediabetes mellitus; Tryptophan metabolism; Two-hour postprandial glucose; Xiaokeqing granules.
©The Author(s) 2025. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, Jia W, Ji L, Xiao J, Shan Z, Liu J, Tian H, Ji Q, Zhu D, Ge J, Lin L, Chen L, Guo X, Zhao Z, Li Q, Zhou Z, Shan G, He J China National Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders Study Group. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1090–1101. - PubMed
-
- Xu Y, Wang L, He J, Bi Y, Li M, Wang T, Wang L, Jiang Y, Dai M, Lu J, Xu M, Li Y, Hu N, Li J, Mi S, Chen CS, Li G, Mu Y, Zhao J, Kong L, Chen J, Lai S, Wang W, Zhao W, Ning G 2010 China Noncommunicable Disease Surveillance Group. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 2013;310:948–959. - PubMed
-
- Braga T, Kraemer-Aguiar LG, Docherty NG, Le Roux CW. Treating prediabetes: why and how should we do it? Minerva Med. 2019;110:52–61. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

