Computer-aided repositioning and functional in vitro assessment of novel PAD4 inhibitors
- PMID: 40697620
- PMCID: PMC12278103
- DOI: 10.1039/d5md00395d
Computer-aided repositioning and functional in vitro assessment of novel PAD4 inhibitors
Abstract
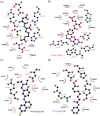
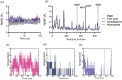
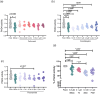
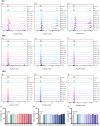
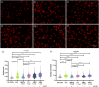
Peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4) is a protein that catalyzes both normal and abnormal citrullination of interacting protein partners, affecting gene regulation and being associated with diseases such as Alzheimer's, cancer, and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). As a result, PAD4 has emerged as a potential therapeutic target; however, no inhibitors have been approved to date. In this study, the REFRAME and ZINC15 drug databases were virtually screened. The approach used molecular docking and dynamics simulation techniques to identify compounds with high-predicted binding affinity to PAD4 (PDB ID: 4DKT). Selected hits from this virtual screening underwent in vitro assays using fixed concentrations derived from the docking score to evaluate their ability to inhibit PAD4 activity, and their effect on neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) release was assessed using an ex vivo human neutrophil model. Computational analyses identified amodiaquine, folic acid, and pyroxamide as stable PAD4 binders. In vitro inhibition assays revealed that amodiaquine (5.0 μM to 1.0 nM) and pyroxamide (0.1 μM) were more potent inhibitors than the reference PAD4 inhibitor BBCla (8.8 μM), while folic acid showed a non-significant trend toward inhibition. Cytotoxicity assays confirmed that all compounds were non-toxic at the tested concentrations, except for amodiaquine at 50 μM. NETosis assays demonstrated that the three selected compounds altered chromatin decondensation and cellular morphology similarly to BBCla, although not uniformly across all cells. Overall, amodiaquine, folic acid, and pyroxamide were identified as PAD4 inhibitors through combined virtual and experimental approaches, supporting their potential as therapeutic candidates for PAD4-related diseases and warranting further investigation.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
References
-
- Koushik S. Joshi N. Nagaraju S. Mahmood S. Mudeenahally K. Padmavathy R. et al., PAD4: pathophysiology, current therapeutics and future perspective in rheumatoid arthritis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2017;21(4):433–447. - PubMed
-
- Thirugnanasambandham I. Jupudi S. Roychowdhury P. Karri V. Madhunapantula S. R. V. Singh S. K. et al., Revamped role for approved drug: integrative computational and biophysical analysis of saquinavir's peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 inhibition for rheumatoid arthritis. Biochem. J. 2024;481(20):1379–1393. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

