Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-induced cholecystitis and cholelithiasis: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis using the FAERS database
- PMID: 40697657
- PMCID: PMC12279493
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1557691
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist-induced cholecystitis and cholelithiasis: a real-world pharmacovigilance analysis using the FAERS database
Abstract
Background: With the widespread use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in managing diabetes and obesity, the occurrence of GLP-1 RA-induced cholecystitis and cholelithiasis has raised increasing concern among healthcare professionals.
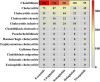
Methods: This study extracted adverse event reports of GLP-1 RA-induced cholecystitis and cholelithiasis from the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System database, covering Q1 2004 to Q2 2024. Disproportionality analysis methods, including the reporting odds ratio, proportional reporting ratio, and Bayesian confidence propagation neural network, were employed to identify associations between GLP-1 RAs and these AEs. The analysis focused on the five most commonly prescribed GLP-1 RAs, evaluated at both high-level term and preferred term levels.
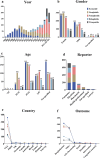
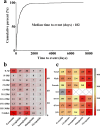
Results: A total of 1,829 reports were identified in which GLP-1 RAs were listed as the primary suspect drug, involving 1,651 patients. All three signal detection methods indicated a positive signal between GLP-1 RAs and these conditions. The majority of cases occurred in patients aged 45 years and older, with a significantly higher prevalence in females. The median onset time of GLP-1 RA-induced cholecystitis and cholelithiasis was 182 days, with variations observed across different drugs, genders, and age groups.
Conclusion: This study provides a comprehensive pharmacovigilance analysis of GLP-1 RA-induced cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, offering valuable insights into the prevention and management of these AEs.
Keywords: FAERS; cholecystitis; cholelithiasis; disproportionality analysis; glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists; pharmacovigilance.
Copyright © 2025 Tao, Zhang, Wan, Zhao, Chen, Wang, Yang, Wang, Ding, Shang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ansari H. U. H., Qazi S. U., Sajid F., Altaf Z., Ghazanfar S., Naveed N., et al. (2024). Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on body weight and cardiometabolic parameters in individuals with obesity and without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr. Pract. 30, 160–171. 10.1016/j.eprac.2023.11.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chong B., Jayabaskaran J., Kong G., Chan Y. H., Chin Y. H., Goh R., et al. (2023). Trends and predictions of malnutrition and obesity in 204 countries and territories: an analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. eClinicalMedicine 57, 101850. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.101850 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

