From radiolabeling to receptor quantification: preclinical assessment of [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol as a cardiac β-adrenoceptor probe
- PMID: 40697658
- PMCID: PMC12280724
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1581598
From radiolabeling to receptor quantification: preclinical assessment of [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol as a cardiac β-adrenoceptor probe
Abstract
Introduction: Accurate cardiac adrenoceptor assessment is crucial for managing cardiovascular diseases. This study introduces a novel radiotracer, technetium-99m-labeled carvedilol ([99mTc]Tc-carvedilol), which advances non-invasive cardiac receptor evaluation by improving traceability and myocardial tissue selectivity. Aimed at strengthening diagnostic precision, it optimizes a selective radioligand for quantifying cardiac adrenergic receptor sites.
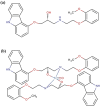
Methods: [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol was synthesized via direct radiolabeling with technetium-99m, key parameters were optimized to maximize radiolabeling efficiency and ensure a reliable and reproducible [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol complex. Biodistribution was rigorously evaluated in vitro and in vivo, emphasizing cardiac uptake, receptor occupancy, biodistribution, and clearance kinetics. Comparative analysis with [131I]iodocarvedilol and 99mTc-sestamibi provided insights into advancements in detection efficiency and translational potential.
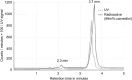
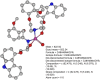
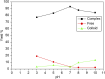
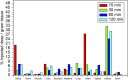
Results: [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol showed a radiolabeling efficiency of 96.5% ± 2.87%, with serum stability >92% at 24 h. Biodistribution studies in Swiss Albino mice (24 mice, aged 10-12 weeks, weighing 25 ± 3 g) revealed peak cardiac uptake (27.533% ± 0.931% injected dose per Gram of tissue (ID/g) within 15 min post-injection, alongside efficient blood clearance and minimal non-target tissue uptake (5.972% ± 0.131% ID/g organ) by 120 min. Docking analysis confirmed robust β1-adrenoceptors (-9.2 kcal/mol) via hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Compared to [131I]iodocarvedilol and 99mTc-sestamibi [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol exhibited superior stability, targeting accuracy, and pharmacokinetics.
Discussion: The enhanced selective cardiac uptake and favorable pharmacokinetics of [99mTc]Tc-carvedilol position it as a promising agent for non-invasive cardiac receptor mapping, with the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy and specificity. Further clinical validation is essential to confirm its efficacy in detecting and evaluating cardiac pathologies.
Keywords: adrenergic receptors; cardiovascular disease; carvedilol; prognostic marker; single-photon emission computed tomography nuclear imaging; technetium-99m.
Copyright © 2025 Azhari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Abdu Hussen A. A. (2022). High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC): a review. Ann. Adv. Chem. 6 (1), 010–020. 10.29328/journal.aac.1001026 - DOI
-
- Al Oraini D. (2018). Calibration of the absolute efficiency of well-type NaI(Tl) scintillation detector in 0.121–1.408 MeV energy range. Sci. Technol. Nucl. Install. 2018, 1–6. 10.1155/2018/6432380 - DOI
-
- Azhari H. F., Hashem A. M. (2024). Quantifying AMPARs with 99mTc-omberacetam: a novel diagnostic radiotracer for ischemic stroke. JUmm Al-Qura Univ. Appll Sci. 10 (1), 211–224. 10.1007/s43994-023-00093-y - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

