Exosomes promise better bone regeneration
- PMID: 40697719
- PMCID: PMC12281136
- DOI: 10.1016/j.reth.2025.06.020
Exosomes promise better bone regeneration
Abstract
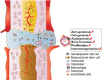
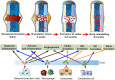
Fractures primarily result from high-energy trauma, leading to structural discontinuity of bone tissue. Contemporary therapeutic approaches continue to face persistent challenges including nonunion, infection, and inflammatory complications that pose significant clinical management difficulties. Emerging evidence demonstrates that extracellular vesicles (EVs), particularly exosomes, serve as critical mediators in diverse pathophysiological processes. Accumulating studies reveal that exosomal cargos enhance osteogenesis and angiogenesis through dynamic regulation of cellular components and molecular networks within the bone remodeling microenvironment, thereby potentiating fracture healing cascades. This comprehensive review systematically examines the mechanistic contributions of exosomes in coordinating osteoblastic differentiation, osteoclastic activity modulation, and neovascularization processes. In addition, we describe the role of exosomes from different cellular sources (e.g., mesenchymal stem cells, endothelial progenitor cells, and osteoblasts) in fracture repair. Finally, this paper elaborates on the potential challenges and future directions for the development of novel exosome-based therapeutic strategies for clinical fracture repair.
Keywords: Exosomes; Extracellular vesicles; Fracture repair; Regeneration.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Liang Y., Xu X., Li X., Xiong J., Li B., Duan L., et al. Chondrocyte-rargeted microRNA delivery by engineered exosomes toward a cell-free osteoarthritis therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36938–36947. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

