Orchiepididymitis as a rare complication of TURP performed four weeks after high-dose-rate brachytherapy for prostate cancer
- PMID: 40697722
- PMCID: PMC12277955
- DOI: 10.5114/jcb.2025.152544
Orchiepididymitis as a rare complication of TURP performed four weeks after high-dose-rate brachytherapy for prostate cancer
Abstract
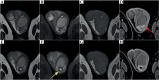
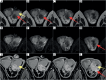
The aim of this paper was to present a rare complication of orchiepididymitis in a patient treated with brachytherapy (BT) for prostate cancer, who underwent trans-ureteral resection of the prostate (TURP) four weeks after BT. A 73-year-old patient with prostate cancer (intermediate-risk group) was eligible for high-dose-rate (HDR) BT combined with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) for 6 months (leuprorelin). Due to increased symptoms, such as urinary retention after BT, the patient required catheterization. Additionally, bacterial inflammation in the lower urinary tract and prostate was present. Due to prolonged micturition disorders, TURP was performed, leading to chronic orchiepididymitis four months after completion of BT and three months after catheter removal following TURP. Due to long-term inflammation, which was resistant to treatment, the left testicle with left epididymis was removed. Unfortunately, inflammatory symptoms occurred post-operatively in the bed and the left groin. Since these symptoms of varying severity continued, anti-inflammatory drugs and analgesics were introduced. TURP performed too quickly after HDR-BT might cause severe complications. Extreme caution regarding TURP should be exercised in patients undergoing BT. Conservative and pharmacological treatment must be introduced in the occurrence of urinary disorders after BT, and any intervention (TURP) should be performed at least 3-6 months after BT. This is especially crucial because of the development of radiation effect over time.
Keywords: HDR-BT; MR; TURP; US examination; brachytherapy; lower urinary tract symptoms; orchiepididymitis; prostate cancer; suprapubic cystostomy; urinary retention.
Copyright © 2025 Termedia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
-
Minimally invasive treatments for lower urinary tract symptoms in men with benign prostatic hyperplasia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Jul 15;7(7):CD013656. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013656.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34693990 Free PMC article.
-
Conservative management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD001843. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001843.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 20;1:CD001843. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001843.pub5. PMID: 22258946 Updated.
-
Conservative management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 20;1(1):CD001843. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001843.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25602133 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hudson JM, Loblaw A, McGuffin Met al. Prostate high dose-rate brachytherapy as monotherapy for low and intermediate-risk prostate cancer: Efficacy results from a randomized phase II clinical trial of one fraction of 19 Gy or two fractions of 13.5 Gy: A 9-year update. Radiother Oncol 2024; 198: 110381. - PubMed
-
- Corkum MT, Achard V, Morton Get al. Ultrahypofractionated radiotherapy for localised prostate cancer: How far can we go? Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2022; 34: 340-349. - PubMed
-
- Hoskin P, Rojas A, Ostler Pet al. Single-dose high-dose-rate brachytherapy compared to two and three fractions for locally advanced prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol 2017; 124: 56-60. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
