The role of ratio markers based on prealbumin in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection
- PMID: 40697817
- PMCID: PMC12279772
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1597401
The role of ratio markers based on prealbumin in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection
Abstract
Background: Periprosthetic joint infection (PJI) is a severe complication following total joint arthroplasty, and the timeliness of its diagnosis and treatment is crucial for patient recovery. Although various biomarkers have been extensively evaluated and applied in clinical practice, the diagnosis of PJI remains challenging. Therefore, it is necessary to identify more precise biomarkers for the diagnosis of PJI. This study aims to investigate the value of ratio-based biomarkers using prealbumin (PA) for the diagnosis of PJI.
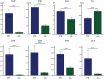
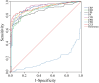
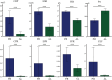
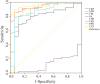
Methods: This study compared the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), fibrinogen (FIB), PA, CRP/PA (CPR), ESR/PA (EPR), FIB/PA (FPR), and the combined ratio of CPR+EPR+FPR(CEF) in 180 patients with PJI and 105 patients with aseptic loosening (AL) who presented at our department from January 2019 to December 2024. The diagnostic efficacy of these markers in PJI diagnosis was assessed using the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve.
Results: Among these biomarkers, CPR has the highest AUC of 0.921 (95%CI 0.890-0.952), and it can distinguish PJI with a cut-off value of 0.0366, a sensitivity of 76.1%, and a specificity of 95.2%. In the diabetic subgroup, the combined biomarker CEF has an AUC of 0.951 for diagnosing PJI, with a sensitivity of 88.9% and a specificity of 94.4%.
Conclusion: Ratio-based markers based on PA show promise as valuable new adjunctive diagnostic markers for PJI.
Keywords: aseptic loosening; diabetes; marker; periprosthetic joint infection; prealbumin.
Copyright © 2025 Cao, Ning, Fan, Cheng, Zhang, Cheng and Dai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
No added value of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet count to mean platelet volume ratio (PC/MPV) over the traditional serum markers (ESR and CRP) in the diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection (PJI).Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025 Jul 13. doi: 10.1002/ksa.12768. Online ahead of print. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2025. PMID: 40652379
-
Plasma D-Dimer Is Noninferior to Serum C-Reactive Protein in the Diagnosis of Periprosthetic Joint Infection.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2023 Apr 5;105(7):501-508. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.22.00784. Epub 2023 Feb 9. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2023. PMID: 36758110
-
Is 18 F-fluoride PET/CT an Accurate Tool to Diagnose Loosening After Total Joint Arthroplasty?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Mar 1;483(3):415-428. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003228. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 39293088
-
Synovial Fluid C-reactive Protein as a Diagnostic Marker for Periprosthetic Joint Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Aug 20;129(16):1987-93. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.187857. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27503025 Free PMC article.
-
The accuracy of D-dimer in the diagnosis of periprosthetic infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2022 Feb 16;17(1):99. doi: 10.1186/s13018-022-03001-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022. PMID: 35172830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chandy S., Joseph K., Sankaranarayanan A., Issac A., Babu G., Wilson B., et al. (2017). Evaluation of c-reactive protein and fibrinogen in patients with chronic and aggressive periodontitis: A clinico-biochemical study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 11, Zc41–Zzc5. doi: 10.7860/jcdr/2017/23100.9552, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Christopher Z. K., McQuivey K. S., Deckey D. G., Haglin J., Spangehl M. J., Bingham J. S. (2021). Acute or chronic periprosthetic joint infection? Using the esr/crp ratio to aid in determining the acuity of periprosthetic joint infections. J. Bone Jt Infect. 6, 229–234. doi: 10.5194/jbji-6-229-2021, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deng L., Wang J., Yang G. Y., Hou Y. Z., Li K. W., Sun B., et al. (2024). Different biomarker ratios in peripheral blood have limited value in diagnosing periprosthetic joint infection after total joint arthroplasty: A single-center, retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 25, 377. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-07499-7, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

