Brucellosis: Bacteriology, pathogenesis, epidemiology and role of the metallophores in virulence: a review
- PMID: 40697821
- PMCID: PMC12279742
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1621230
Brucellosis: Bacteriology, pathogenesis, epidemiology and role of the metallophores in virulence: a review
Abstract
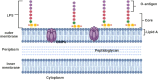
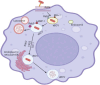
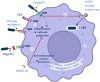
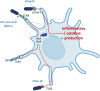
Brucellosis is a recognized zoonotic disease caused by various Brucella species with significant economic and animal welfare ramifications worldwide. The spread of brucellosis from domestic livestock and wild animals, as well as its emergence in new regions, present novel epidemiological challenges. The consumption of unpasteurized milk and dairy products from unsanitary farms in endemic areas poses a serious risk to public health from brucellosis. Determining the accurate prevalence of brucellosis, particularly in regions with persistently high prevalence, basically requires careful and frequent surveillance. Furthermore, transmission and detection of the illness in non-endemic areas have become more complex due to global human and animal migration as well as the trade in animal products. This review presents an updated understanding of brucellosis, covering its classification and taxonomy, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment approaches, epidemiology, available control and prevention measures, antimicrobial resistance and the role of metal uptake in bacterial virulence. It highlights the consequences of brucellosis for global health and underscores the need for continuous research, knowledge sharing, and interdisciplinary cooperation for effective disease control and prevention.
Keywords: Brucella; brucellosis; livestock; public health threats; zoonotic disease.
Copyright © 2025 Ghssein, Ezzeddine, Tokajian, Khoury, Kobeissy, Ibrahim, Iskandar and Hassan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

