Transcriptomic signatures of neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome in a prospective cohort of respiratory distress
- PMID: 40697828
- PMCID: PMC12281067
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.113007
Transcriptomic signatures of neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome in a prospective cohort of respiratory distress
Abstract
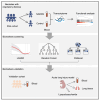
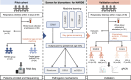
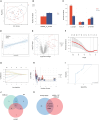
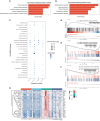
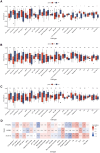
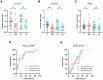
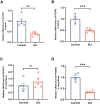
Neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome (NARDS) is challenging to differentiate from other respiratory conditions, and gestational age (GA) may influence gene expression. This study characterized whole blood transcriptomic profiles of NARDS in a pilot cohort of 48 neonates with respiratory distress, demonstrating a significant GA-dependent modulation of gene expression. Functional analyses revealed prominent involvement of interferon-related pathways in NARDS, with greater suppression in neonates born before 34 weeks. Immune cell infiltration was observed in term or late preterm neonates but was absent in more preterm cases. Machine learning identified three key predictive genes, among which ALOX15 and PTGDR2 were validated in an independent cohort, with area under the curve ranging from 0.68 to 0.83 across different GAs. The gene changes were also confirmed in a neonatal lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury mouse model. These findings highlight the potential predictive and therapeutic value of ALOX15 and PTGDR2 for NARDS.
Keywords: Machine learning; Transcriptomics.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Khemani R.G., Smith L.S., Zimmerman J.J., Erickson S., Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference Group Pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: definition, incidence, and epidemiology: proceedings from the Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 2015;16:S23–S40. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000432. - DOI - PubMed
-
- De Luca D., van Kaam A.H., Tingay D.G., Courtney S.E., Danhaive O., Carnielli V.P., Zimmermann L.J., Kneyber M.C.J., Tissieres P., Brierley J., et al. The Montreux definition of neonatal ARDS: biological and clinical background behind the description of a new entity. Lancet Respir. Med. 2017;5:657–666. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(17)30214-X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Li J., Shi Y., Chinese Neonatal ARDS ChiNARDS study group Clinical characteristics and outcomes in neonates with perinatal acute respiratory distress syndrome in China: a national, multicentre, cross-sectional study. eClinicalMedicine. 2023;55 doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101739. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

