Association between waist circumference and fatty liver disease in older adult population: a cross-sectional study in Urumqi
- PMID: 40697841
- PMCID: PMC12279773
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1620261
Association between waist circumference and fatty liver disease in older adult population: a cross-sectional study in Urumqi
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to explore the correlation between waist circumference and the prevalence of fatty liver disease in the older adult population in Urumqi.
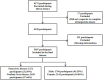
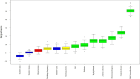
Methods: Through cluster random sampling of healthcare institutions within the urban districts of Urumqi, a final cohort of 3,907 participants was enrolled from three institutions. In addition, the informed consent forms of the participants were obtained. Chi-square tests were used for univariate analysis between groups, and the data were divided into a training set and a test set in a 7:3 ratio. Variables were further screened using machine learning models such as random forest classifier and Lasso. Logistic regression and restricted cubic spline models were used to analyze the correlation between waist circumference and fatty liver disease.
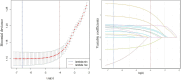
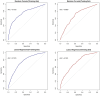
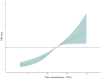
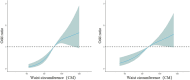
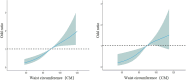
Results: The prevalence of fatty liver disease was 32.56%, with 31.54% in men and 33.40% in women. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that compared with non-central obesity, the risk of fatty liver disease in central obesity was significantly higher (OR = 1.768, 95% CI: 1.481-2.112). The restricted cubic spline model analysis showed that the risk of fatty liver disease increased with waist circumference in the older adult population. In the total population and the male group, waist circumference and central obesity showed a nonlinear relationship, while in the female group, those below 75 years old, and those 75 and older, a linear relationship was observed.
Conclusion: Controlling waist circumference is important for the prevention of fatty liver disease. The older adult population in Urumqi should pay attention to the risks posed by increasing waist circumference.
Keywords: fatty liver; machine learning; older adult population; restricted cubic spline; waist circumference.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhao and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

