Global, regional, and national burden and trends of syphilis among women of childbearing age from 1990 to 2021
- PMID: 40697850
- PMCID: PMC12279697
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1580964
Global, regional, and national burden and trends of syphilis among women of childbearing age from 1990 to 2021
Abstract
Background: Syphilis represents a significant sexual health concern for women of childbearing age (WCBA) worldwide. However, information regarded the burden and trends associated with this disease is limited. This study aimed to evaluate the changes in syphilis burden among WCBA aged 15-49 years from 1990 to 2021 at global, regional, and national levels.
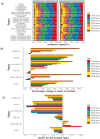
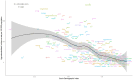
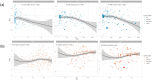
Methods: The extensive information was gathered from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2021 database concerning the incidence, prevalence, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) related to syphilis in WCBA aged 15-49 across 204 countries and territories from 1990 to 2021. To quantify temporal trends, the estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) was calculated in age-standardized rate (ASR) for incidence, prevalence, and DALYs based on age group, region, and sociodemographic index (SDI). The relationship between ASR and SDI was examined using spearman correlation analysis.
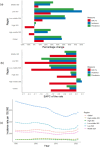
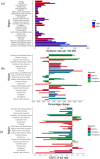
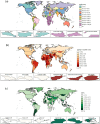
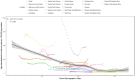
Results: In 2021, there were 20.48 million prevalent cases, 5.36 million new syphilis cases, and 39.59 thousand DALYs among WCBA, reflecting increases of 45.85, 46.96, and 16.08%, respectively, since 1990. Over 32 years, global rates of prevalence, incidence, and DALYs declined, with EAPCs of -0.50, -0.35, and -1.30. However, high-middle SDI regions experienced rising trends in incidence (EAPC: 0.28) and prevalence (EAPC: 0.22). The Low-middle SDI region had the highest syphilis cases among WCBA, accounting for about one-third of the global total. Notably, the 20-24 age group had the highest incidence rate at 467.35 per 100,000.
Conclusion: Our findings highlight a decline in the global prevalence of syphilis from 1990 to 2021, the burden of this disease remains significant in low-and middle-income countries and regions. The development of more effective strategies to prevent and reduce the burden of syphilis is a pressing need.
Keywords: age-standardized rate; burden of disease; estimated annual percentage change; syphilis; women of childbearing age.
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Ye, Li and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Musculoskeletal disorders in women of childbearing age: global trends, socio-demographic disparities, and future projections.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2532860. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2532860. Epub 2025 Jul 20. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40684443 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive analysis of trends and inequalities in rheumatoid arthritis burden among women of childbearing age: insights from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2025 Jul;43(7):1321-1331. doi: 10.55563/clinexprheumatol/r9rruc. Epub 2025 May 8. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40371555
-
Global, regional, and national burden of maternal disorders, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis from the global burden of disease study 2021.BMC Public Health. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):2576. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-23814-w. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40730990 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden and risk factors of musculoskeletal disorders among adolescents and young adults in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019.Autoimmun Rev. 2023 Aug;22(8):103361. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103361. Epub 2023 May 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2023. PMID: 37230312 Review.
-
Burden of inflammatory bowel disease among elderly, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis based on the global burden of disease study 2019.Autoimmun Rev. 2025 Jan 31;24(2):103708. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103708. Epub 2024 Nov 23. Autoimmun Rev. 2025. PMID: 39586389
References
-
- Comfort H, McHugh TA, Schumacher AE, Harris A, May EA, Paulson KR, et al. Global, regional, and national stillbirths at 20 weeks' gestation or longer in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2021: findings from the global burden of disease study 2021. Lancet. (2024) 404:1955–88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)01925-1, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fu L, Sun Y, Han M, Wang B, Xiao F, Zhou Y, et al. Incidence trends of five common sexually transmitted infections excluding hiv from 1990 to 2019 at the global, regional, and national levels: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. Front Med. (2022) 9:851635. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.851635, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

