Evolutionary dynamics of the calcium/cation antiporter superfamily in Brassicaceae: codon usage, selection pressure, and BnCaCAs role in abiotic stress response
- PMID: 40697863
- PMCID: PMC12279817
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2025.1506461
Evolutionary dynamics of the calcium/cation antiporter superfamily in Brassicaceae: codon usage, selection pressure, and BnCaCAs role in abiotic stress response
Abstract
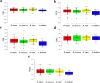
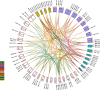
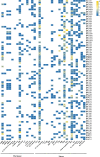
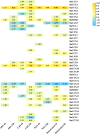
Calcium (Ca2+) serves as a crucial intracellular messenger in plant signaling, particularly during stress responses. Precise regulation of calcium levels by transporters such as calcium/cation (CaCA) antiporters is essential for its effective function. However, the evolutionary dynamics and stress-related roles of the CaCA superfamily remain underexplored in key Brassicaceae crops. This study aimed to address this gap by investigating the hypothesis that CaCA genes in Brassica napus, B. rapa, and B. oleracea have undergone distinct evolutionary trajectories influencing their roles in abiotic stress responses, using Arabidopsis thaliana for comparison. Using Hidden Markov Model (HMM) profiling, 93 CaCA genes were identified across these species. These genes were categorized into four phylogenetic clades: CAX, CCX, NCL, and MHX. Comprehensive analyses of their coding proteins physicochemical properties, subcellular localization, conserved motifs, and gene structures were performed. Codon usage bias (CUB) analysis showed CaCA genes have low codon bias and CUB indices indicated a complex interplay between mutational and selective pressures, highlighting the influence of natural selection and mutational biases in shaping these genes. Collinearity and duplication analyses highlighted the evolutionary dynamics of the CaCA gene family, with several segmental and whole-genome duplication (WGD) events contributing to their expansion. Notably, duplicated genes underwent negative selection pressure, which removed harmful mutations, resulting in slower evolution and maintaining the functional stability of CaCA genes throughout their evolutionary history. Analysis of cis-regulatory elements (CREs) revealed their responsiveness to hormones and stresses, suggesting a potential role in plant environmental adaptation. Expression profiling of CaCA genes under abiotic stresses (dehydration, salinity, cold, and ABA) in B. napus was performed using publicly available RNA-seq datasets and analyzed with standard bioinformatics tools. Based on the results of expression analysis, key CaCA genes, such as BnCAX3, BnCAX16, BnCC2, BnCCX9, BnCAX5, BnCAX12, BnCAX13, and BnMHX1, which are differentially expressed and potentially crucial for stress tolerance. This comprehensive study elucidates the evolutionary architecture of the CaCA gene family in Brassicaceae and identifies key BnCaCA genes potentially crucial for abiotic stress tolerance, thus offering a foundation for future functional studies aimed at improving crop resilience.
Keywords: bioinformatics; calcium homeostasis; codon usage bias; evolution; stress.
Copyright © 2025 Abedi, Pourkarimi Daryakenari, Zare, Allahi and Hajiahmadi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Andrews S., Krueger F., Segonds-Pichon A., Biggins L., Krueger C., Wingett S. (2010). FastQC. A quality control tool for high throughput sequence data 370. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

