The comparison of remimazolam and midazolam in bronchoscopic sedation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40697921
- PMCID: PMC12279844
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1581280
The comparison of remimazolam and midazolam in bronchoscopic sedation: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Effective sedation is critical for bronchoscopy, ensuring patient comfort and procedural success. Midazolam, though widely used, has limitations such as longer induction and recovery times. Remimazolam, a novel ultra-short-acting benzodiazepine, offers rapid onset, faster recovery, and a safer profile, making it a potential alternative.
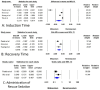
Study design and methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis of four randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 630 patients compared remimazolam with midazolam for bronchoscopy sedation. Primary outcomes included induction time, recovery time, and rescue sedation rates. Secondary outcomes assessed procedural duration and adverse events. Random-effects models were used for analysis, and evidence quality was graded using GRADE criteria.
Results: Remimazolam reduced induction time by 3.2 min (95% CI: -5.51 to -0.91, p = 0.006) and recovery time (SMD: -0.976, 95% CI: -1.48 to -0.47, p < 0.001) compared to midazolam. Patients receiving remimazolam required less rescue sedation (OR: 0.223, 95% CI: 0.107 to 0.467, p < 0.001). No significant differences were observed in bronchoscopy duration or the incidence of intraoperative and postoperative complications, including hypoxia, hypotension, and nausea.
Conclusion: Remimazolam may reduce induction and recovery times and decrease the need for rescue sedation compared to midazolam. However, due to high heterogeneity and the limited number of studies, these findings should be interpreted with caution. Due to the limited number of studies and observed heterogeneity, further high-quality trials are necessary to confirm these findings.
Clinical trial registration: Clinicaltrial.gov, identifier: CRD42024623846.
Keywords: bronchoscopy; meta-analysis; midazolam; remimazolam; sedation; systematic review.
Copyright © 2025 AbuJwaid, Deeb, Amro and Asbeh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacological agents for procedural sedation and analgesia in patients undergoing gastrointestinal endoscopy: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.EClinicalMedicine. 2025 Jun 16;85:103307. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2025.103307. eCollection 2025 Jul. EClinicalMedicine. 2025. PMID: 40599871 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous midazolam infusion for sedation of infants in the neonatal intensive care unit.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD002052. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002052. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jun 13;(6):CD002052. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002052.pub2. PMID: 12535424 Updated.
-
Haloperidol plus promethazine for psychosis-induced aggression.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 25;11(11):CD005146. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005146.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27885664 Free PMC article.
-
Chloral hydrate as a sedating agent for neurodiagnostic procedures in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Nov 3;11(11):CD011786. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011786.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 16;8:CD011786. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011786.pub3. PMID: 29099542 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- D'Andria Ursoleo J, Bottussi A, Agosta VT, Monaco F. Letter to the editor regarding "effect of remimazolam versus propofol on hypotension after anesthetic induction in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: a randomized controlled trial". J Clin Anesth. (2024) 99:111644. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2024.111644, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

