Potential active ingredients and mechanisms of Shufeitie ointment in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by integrating transdermal chemistry and network pharmacology
- PMID: 40697927
- PMCID: PMC12279505
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1605372
Potential active ingredients and mechanisms of Shufeitie ointment in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by integrating transdermal chemistry and network pharmacology
Abstract
Purpose: This study aims to identify the transdermal penetration components of Shufeitie ointment (SFTOT) and investigate the potential active components and mechanisms through which SFTOT exerts its effects on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
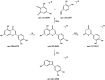
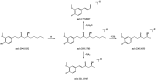
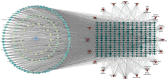
Methods: An in vitro permeation test (IVPT) of SFTOT was conducted using a modified Franz diffusion cell method. Ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/electrostatic field orbitrap high-resolution mass spectrometry (UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS) was employed to analyze data from the transdermal receiving solution, enabling comprehensive identification of the components that permeate through the skin. To predict the potential mechanisms by which SFTOT may treat COPD, network pharmacology was used to construct a component-target-collaterals network. Additionally, molecular docking was applied to verify the interactions between the potential transdermal active components of SFTOT and the core targets.
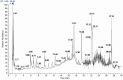
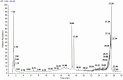
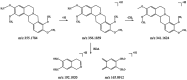
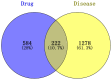
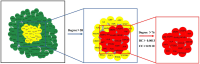
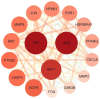
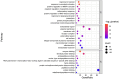
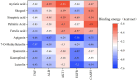
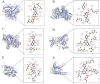
Results: Using UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap/MS, we identified 129 transdermal permeation components in SFTOT. Network pharmacology analysis revealed 222 common targets between SFTOT and COPD. The primary active components were predicted to be luteolin, kaempferol, quercetin, 7-O-methylluteolin, apigenin, ferulic acid, palmitic acid, inapinic acid, 6-shogaol, and myristic acid. These components were primarily enriched in the AGE-RAGE, TNF, PI3K-Akt, and MAPK signaling pathways. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis identified TNF, ALB, AKT1, EGFR, and CASP3 as core targets. Molecular docking results showed that 72% of component-target interactions had a binding energy of < -5.0 kcal/mol, indicating strong binding activity. Among these, apigenin exhibited the lowest binding energy with EGFR and consistently lower binding energies with other core targets compared to the other components. This suggests that apigenin may play a key role in treatment.
Conclusion: High-resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry effectively identified the transdermal penetration components of SFTOT, providing a foundation for further screening of key active compounds. Our findings suggest that SFTOT may alleviate COPD by downregulating TNF, ALB, AKT1, EGFR, and CASP3 while inhibiting inflammatory mediator release through the AGE-RAGE, TNF, PI3K-Akt, and MAPK signaling pathways. These effects may help reduce COPD-related symptom clusters. Notably, apigenin appears to be a crucial bioactive component in the prevention and treatment of COPD.
Keywords: Franz diffusion cell; Shufeitie ointment; UHPLC-Q-orbitrap/MS; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; external preparations; network pharmacology.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Zhang, Wang, Shi, Xue, Zhang, Wang, Gui, Li, Li, Li and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Elucidating the Mechanism of Xiaoqinglong Decoction in Chronic Urticaria Treatment: An Integrated Approach of Network Pharmacology, Bioinformatics Analysis, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025 Jul 16. doi: 10.2174/0115734099391401250701045509. Online ahead of print. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40676786
-
The Potential Mechanisms of Banxia Xiexin Decoction in Treating Chronic Colitis: Insights from UPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and Network Pharmacology Studies.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025 Jul 14. doi: 10.2174/0113862073350796250305225907. Online ahead of print. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 40662553
-
Investigation of the effect and mechanism of Fei Re Pu Qing powder in treating acute lung injury (ALI) by modulating macrophage polarization via serum pharmacology and network pharmacology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120089. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120089. Epub 2025 Jun 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40499803
-
Computer and mobile technology interventions for self-management in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 23;5(5):CD011425. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011425.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28535331 Free PMC article.
-
Self-management interventions including action plans for exacerbations versus usual care in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Aug 4;8(8):CD011682. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011682.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28777450 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Safiri S, Carson-Chahhoud K, Noori M, Nejadghaderi SA, Sullman M, Ahmadian HJ, et al. Burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: results from the global burden of disease study 2019. BMJ. (2022) 378:e69679. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2021-069679 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

