Decorin levels and cardiometabolic function after endurance exercise
- PMID: 40697980
- PMCID: PMC12279853
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1546370
Decorin levels and cardiometabolic function after endurance exercise
Abstract
Introduction: Decorin is secreted from myotubes in response to exercise and plays a vital role in repairing and regenerate skeletal and cardiac muscle. The role of decorin levels in cardiometabolic function after endurance exercise was investigated.
Methods: Fifty-six male amateur runners, aged 30 to 55 years, participated in this study. Plasma decorin levels were determined and cardiopulmonary exercise test (CPET) was performed using a breath-by-breath system before and after the marathon.
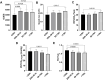
Results: Correlations between decorin levels and CPET parameters were assessed using Spearman's rank correlation test. Runners were categorized into percentiles based on decorin concentrations, and group differences were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's post hoc multiple comparisons.We observed impairments in peak VO2 and in the Oxygen Uptake Efficiency Slope (OUES) following the race. Plasma decorin levels increased approximately two-fold immediately after the race. Post-race decorin concentrations were positively correlated with maximum speed (km/h), VO2 (mL/kg/min), VE/VCO2, VE/VCO2 slope, OUES, and the rate of change in VE/VCO2 and VE/VCO2 slope. Runners with plasma decorin levels below the 25th percentile exhibited significantly lower OUES, while those above the 75th percentile demonstrated higher maximum speed, VE/VCO2, rate of change in VE/VCO2 slope, and VCO2 compared to individuals in the lowest quartile.
Discussion: Overall, decorin levels were associated with several CPET parameters, suggesting that runners with varying decorin concentrations may exhibit distinct respiratory and/or metabolic profiles. The potential influence of an elevated VE/VCO2 slope on cardiometabolic responses in runners with higher decorin levels warrants further investigation.
Keywords: decorin; exercise; metabolism; myokine; performance.
Copyright © 2025 de Fontes-Junior, de Sousa, de Oliveira, Sierra and Cury-Boaventura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prediction of severe cardiovascular events by VE/VCO2 slope versus peak VO2 in systolic heart failure: a meta-analysis of the published literature.Am Heart J. 2010 Dec;160(6):1004-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.08.037. Am Heart J. 2010. PMID: 21146651
-
Prediction of left ventricular reverse remodeling in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction using cardiopulmonary exercise testing.J Cardiol. 2025 Aug;86(2):164-171. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2025.01.021. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39921051
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation versus usual care for adults with asthma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 22;8(8):CD013485. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013485.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35993916 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic respiratory parameters in heart failure patients with and without exercise oscillatory ventilation - a systematic review and descriptive meta-analysis.Int J Cardiol. 2015 Mar 1;182:476-86. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.01.029. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Int J Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25616233
-
Acute effects of isolated and combined dietary nitrate and caffeine ingestion on ergometer-based 1000 m time trial performance in highly trained kayakers.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2459095. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2025.2459095. Epub 2025 Feb 18. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 39967381 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

