Effect of a saffron extract on sleep quality in adults with moderate insomnia: A decentralized, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 40698027
- PMCID: PMC12281372
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sleepx.2025.100147
Effect of a saffron extract on sleep quality in adults with moderate insomnia: A decentralized, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Aim: Natural interventions for sleep disturbances, such as saffron extract, are gaining scientific and clinical interest. This 3-arm, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial examined the effect of a standardized saffron extract (Safr'Inside™) on sleep, stress, and other associated psychological outcomes in 165 adults reporting moderate insomnia.
Methods: Participants received 30 mg, 20 mg saffron extract, or placebo for 4 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in insomnia symptoms (Athens Insomnia Scale, AIS). Secondary outcomes were the Single-Item Sleep Quality Scale (SQS), Perceived Stress Scale (PSS), Patient Health Questionnaire-4 (PHQ-4), Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS), Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS), and World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL). Analyses followed an intention-to-treat (ITT) approach, with per-protocol (PP) confirmation.
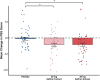
Results: Among 150 completers, saffron extract led to a greater reduction in insomnia symptoms (AIS) than the placebo (between-group adjusted mean difference β = -0.95 [95 % CI: -1.79, -0.11], P < .05). In secondary analyses, sleep quality (SQS) improved significantly after 3 weeks and was sustained at week 4 in both saffron groups compared to placebo (30 mg vs placebo: β = 0.82 [95 % CI: 0.22, 1.41], P = .004; 20 mg vs placebo: β = 1.02 [0.43, 1.62], P < .001). Perceived stress (PSS) was significantly reduced with 30 mg or 20 mg saffron extract compared to placebo (30 mg vs placebo: β = -1.87 [95 % CI: -3.23, -0.53], P = .01; 20 mg vs placebo: β = -1.89 [95 % CI: -3.22, -0.52], P = .04). Some improvement in psychological symptoms (PHQ-4) was also observed with 30 mg saffron extract compared to placebo (β = -0.79 [-1.40, -0.18], P = .03). All other measures showed no significant differences. No serious adverse events occurred.
Conclusions: Four weeks of 20 or 30 mg saffron extract may reduce insomnia and stress in middle-aged adults. Future research should assess longer interventions and explore which subgroups benefit most from saffron extract.
Keywords: Athens insomnia scale; Decentralized trial; Insomnia; Mental health; Randomized controlled trial; Saffron extract; Sleep.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Andreas Hahn reports financial support was provided by Activ’Inside SAS. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Matsumoto T., Chin K. Prevalence of sleep disturbances: sleep disordered breathing, short sleep duration, and non-restorative sleep. Respir Investig. 2019;57(3):227–237. PMID:30827934. - PubMed
-
- Ohayon M.M. Epidemiological overview of sleep disorders in the general population. Sleep Med Res. 2011;2(1):1–9. doi: 10.17241/smr.2011.2.1.1. - DOI
-
- Edinger J.D., Arnedt J.T., Bertisch S.M., Carney C.E., Harrington J.J., Lichstein K.L., Sateia M.J., Troxel W.M., Zhou E.S., Kazmi U., Heald J.L., Martin J.L. Behavioral and psychological treatments for chronic insomnia disorder in adults: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2021;17(2):255–262. PMID:33164742. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

