Recapitulation of in vivo angiogenesis and osteogenesis within an ex vivo muscle pouch-based coral-derived macroporous construct organoid model
- PMID: 40698067
- PMCID: PMC12282400
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.04.002
Recapitulation of in vivo angiogenesis and osteogenesis within an ex vivo muscle pouch-based coral-derived macroporous construct organoid model
Abstract
Background: Segmental bone defect is a challenging clinical problem that often requires autologous bone grafting, which has limitations such as donor site morbidity and insufficient supply. Bone tissue engineering aims to create functional bone substitutes that can mimic the properties and processes of native bone. However, the discrepancy between in vitro and in vivo conditions hinders the successful translation of bone tissue engineering from animal models to human applications. Organoids, such as muscle pouch-based models, are emerging as promising tools that can closely resemble the osteogenic niche and overcome some of the limitations of conventional in vitro models.
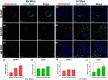
Methods: In this study, we explored two distinct muscle-biomaterial based bone induction models: an in vivo heterotopic implantation model and a novel ex vivo muscle pouch-based coral-derived macroporous construct organoid model. They both utilized the coral-derived constructs, specifically 13 % hydroxyapatite/calcium carbonate (13 % HA/CC) as the biomaterial. We implanted 72 coral-derived devices into rats' rectus abdominis muscle, divided equally between in vivo and ex vivo groups. Samples were harvested at 15, 30, and 60 days for molecular and histological analyses. We assessed the relative gene expression of angiogenesis markers (Vegfa and Col4a1) and osteogenesis signaling and structural markers (Runx2, Bmp2, Ocn and Alp) using qRT-PCR. We analyzed tissue morphogenesis, angiogenesis and induction of bone formation by H&E and modified Goldner's Trichrome staining. Immunostaining was further used to detect the expression and localization of OCN, VEGFA and CD31 in both in vivo and ex vivo models.
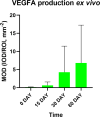
Results: We demonstrated that ex vivo muscle pouch-based coral-derived macroporous construct organoid model supported tissue survival up to 60 days with compromised tissue ingrowth compared to the in vivo model. Primary vascular structures formed at the tissue-scaffold interface in the organoid system with persistent up-regulation of Vegfa and Col4a1, while comprehensive angiogenesis took place with early up-regulation of Vegfa and Col4a1 in vivo. Proper bone formation was absent in both the ex vivo and in vivo models, but the in vivo models showed an up-regulation of Bmp2 and Alp in early phase and a delayed Ocn expression on day 30. The ex vivo model showed connective tissue formation, comprehensive OCN deposition, and gene expression patterns mimicking in vivo trends but with some distinctions.
Conclusions: The ex vivo muscle pouch-based coral-derived macroporous construct organoid model in this study can partially recapitulate angiogenesis and osteogenesis as compared to the in vivo model. However, key molecular signaling events that regulate these processes remained inactive. The study demonstrated that activating these events could enable the establishment of an ex vivo tissue-based vascularized model.
The translational potential of this article: This study partly elucidated the molecular signaling events involved in the development of an ex vivo tissue-based osteogenic organoid that closely resembled its in vivo counterpart. This would facilitate the development of well vascularized artificial bone grafts for treating segmental bone defects.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Coral-derived construct; Muscle pouch-based; Organoids; Osteogenesis.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Huggins C.B. The formation of bone under the influence of epithelium of the urinary tract. Arch Surg. 1931;22(3):377–408.
-
- Levander G. A study of bone regeneration surgery. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1938;67:705–712.
-
- Lacroix P. Recent investigations on the growth of bone. Nature. 1945;156(3967) 576-76.
-
- Urist M.R. Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965;150(3698):893–899. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

