Allogeneic CAR-engineered cellular therapy for relapsed and refractory large B cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40698082
- PMCID: PMC12279871
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1585556
Allogeneic CAR-engineered cellular therapy for relapsed and refractory large B cell lymphoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Introduction: Relapsed/refractory (r/r) large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) remains a difficult-to-treat disease with limited treatment options and high unmet clinical need, necessitating the development of new therapies with greater potency and broader applicability. While autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapies have transformed the treatment landscape, 60-65% of patients receiving these therapies eventually relapse, underscoring the need for improved approaches. Allogeneic CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapies have recently emerged as promising alternatives, offering the potential to shorten manufacturing times, reduce costs, and expand access to a broader patient population. This systematic review and meta-analysis compiles the currently available clinical trial data on the efficacy and safety of these novel therapies in adult patients with r/r LBCL.
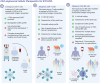
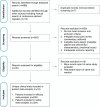
Methods: A systematic search of MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials was conducted for studies published up to January 12, 2025, involving allogeneic CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapies in R/R LBCL. The primary outcomes assessed were the best overall response rate (bORR) and best complete response rate (bCRR) at any time point. Secondary outcomes included rates of grade 1-2 and grade 3+ cytokine release syndrome (CRS), grade 1-2 and grade 3+ immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS), grade 1-2 and grade 3+ infections and incidence of graft-versus-host disease (GvHD).
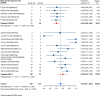
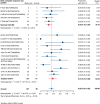
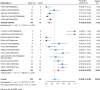
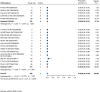
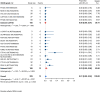
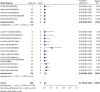
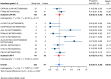
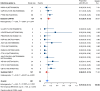
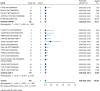
Results: Nineteen studies met the inclusion and exclusion criteria, encompassing 334 patients (155 CAR-NK; 179 CAR-T) evaluable for safety and 235 patients evaluable for response (77 CAR-NK; 158 CAR-T). The pooled estimates for the best overall response rate (bORR) and the best complete response rate (bCRR) were 52.5% [95% CI, 41.0-63.9] and 32.8% [95% CI, 24.2-42.0], respectively. Safety analysis revealed very low incidences of grade 3+ CRS (0.04% [95% CI 0.00-0.49]) or grade 3+ ICANS (0.64% [95% CI 0.01-2.23]) and only one occurrence of a GvH-like reaction across 334 infused patients enrolled in the included studies, highlighting the remarkable safety profile of CAR-engineered "off-the-shelf" allogeneic approaches. The estimated overall incidence of low-grade CRS was 30% [95% CI, 14-48], while the estimated overall incidence of low-grade ICANS was 1% [95% CI, 0%-4%], markedly lower than current-generation autologous CAR-T cell products. The incidence of low-grade and severe infections was 25% [95% CI 14-36%) (n=252) and 7% [95% CI 2-14%] (n=291), respectively.
Discussion: Together, allogeneic CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapies demonstrate encouraging efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with r/r LBCL. Coupled with their favorable safety profiles and the potential for off-the-shelf availability, allogeneic cell therapies hold great promise to broaden the reach of live cell-based treatments, delivering impactful results to a wider patient population in the coming years.
Keywords: CRISPR gene editing; adoptive cell therapy (ACT); allogeneic CAR-NK cells; allogeneic CAR-T cells; cellular engineering; clinical trial; large B cell lymphoma; precision gene editing.
Copyright © 2025 Biederstädt, Bassermann and Hecker.
Conflict of interest statement
JH provided consulting services and received honoraria from Johnson & Johnson, BMS, Kite/Gilead, Abbvie, Servier, Novartis, Roche, Iovance, Imatics, Philogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Immunocore, Autolus, Kyverna. AB declares the absence of any commercial or financial conflict of interest. FB received honoraria from Johnson & Johnson, BMS, Amgen and GSK.
Figures
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380(1):45–56. - PubMed
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. (2020) 396(10254):839–52. - PubMed
-
- Schuster SJ, Tam CS, Borchmann P, Worel N, McGuirk JP, Holte H, et al. Long-term clinical outcomes of tisagenlecleucel in patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive B-cell lymphomas (JULIET): A multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. (2021) 22(10):1403–15. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00375-2, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Locke FL, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Perales M-A, Kersten M-J, Oluwole OO, et al. Axicabtagene ciloleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. (2022) 386(7):640–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

