Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and drug delivery systems for tumor
- PMID: 40698124
- PMCID: PMC12278421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.04.033
Extracellular vesicles as biomarkers and drug delivery systems for tumor
Abstract
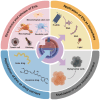
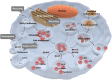
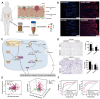
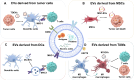
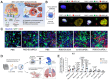
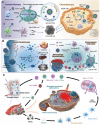
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are crucial for facilitating intercellular communication, promoting cell migration, and orchestrating the immune response. Recently, EVs can diagnose and treat tumors. EVs can be measured as biomarkers to provide information about the type of disease and therapeutic efficacy. Furthermore, EVs with lower immunogenicity and better biocompatibility are natural carriers of chemicals and gene drugs. Herein, we review the molecular composition, biogenesis, and separation methods of EVs. We also highlight the important role of EVs from different origins as biomarkers and drug delivery systems in tumor therapy. Finally, we provide deep insights into how EVs play a role in reversing the immunosuppressive microenvironment.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Drug delivery systems; Drug loading methods; Extracellular vesicles; Molecular composition; Separation technologies; Tumor immunotherapy; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Systematic proteomic and small RNA profiling of extracellular vesicles from cattle infected with a naturally occurring buparvaquone-resistant strain of Theileria annulata and from uninfected controls.Parasit Vectors. 2025 Jun 10;18(1):221. doi: 10.1186/s13071-025-06834-8. Parasit Vectors. 2025. PMID: 40495253 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular communication between extracellular vesicles from conditioned macrophages and breast cancer cells drives endocrine therapy resistance.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 3;13:1548724. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1548724. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40567500 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Populations of Extracellular Vesicles with Opposite Functions during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Infection.J Virol. 2021 Feb 24;95(6):e02357-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02357-20. Print 2021 Feb 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33361424 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles in the immune microenvironment of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Foe or future?J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024 Sep;125(4):101738. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2023.101738. Epub 2023 Dec 12. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38097013 Review.
-
Approaches to incorporate extracellular vesicles into exposure science, toxicology, and public health research.J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2022 Sep;32(5):647-659. doi: 10.1038/s41370-022-00417-w. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol. 2022. PMID: 35217808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pitt J.M., Marabelle A., Eggermont A., Soria J.C., Kroemer G., Zitvogel L. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: removing obstruction to anticancer immune responses and immunotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1482–1492. - PubMed
-
- Feng J., Xiu Q., Huang Y., Troyer Z., Li B., Zheng L. Plant-derived vesicle-like nanoparticles as promising biotherapeutic tools: present and future. Adv Mater. 2023;35 - PubMed
-
- van Niel G., Carter D.R.F., Clayton A., Lambert D.W., Raposo G., Vader P. Challenges and directions in studying cell-cell communication by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2022;23:369–382. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

