Trends in intestinal aging: From underlying mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 40698139
- PMCID: PMC12278430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.011
Trends in intestinal aging: From underlying mechanisms to therapeutic strategies
Abstract
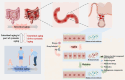
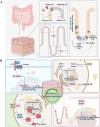
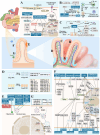
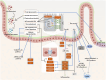
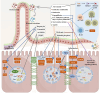
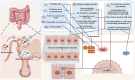
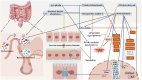
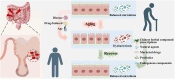
Intestinal aging is central to systemic aging, characterized by a progressive decline in intestinal structure and function. The core mechanisms involve dysregulation of epithelial cell renewal and gut microbiota dysbiosis. In addition to previous results in model organisms like Drosophila melanogaster, recent studies have shown that in mammalian models, aging causes increased intestinal permeability and intestinal-derived systemic inflammation, thereby affecting longevity. Therefore, anti-intestinal aging can be an important strategy for reducing frailty and promoting longevity. There are three key gaps remaining in the study of intestinal aging: (1) overemphasis on aging-related diseases rather than the primary aging mechanisms; (2) lack of specific drugs or treatments to prevent or treat intestinal aging; (3) limited aging-specific dysbiosis research. In this review, the basic structures and renewal mechanisms of intestinal epithelium, and mechanisms and potential therapies for intestinal aging are discussed to advance understanding of the causes, consequences, and treatments of age-related intestinal dysfunction.
Keywords: Cross-talk; Intestinal aging; Intestinal epithelial renewal; Intestinal permeability; Intestine-derived systemic inflammation; Mechanism; Stem cell; Therapeutic strategy.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Figdraw and BioRender were used to create the figures.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Guidelines for the prevention and management of bronchial asthma (2024 edition)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 12;48(3):208-248. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20241013-00601. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40050074 Chinese.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Synbiotics, prebiotics and probiotics for solid organ transplant recipients.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 20;9(9):CD014804. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014804.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36126902 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Chang J.Y., Park S.J., Park J.J., Kim T.I., Cheon J.H., Park J. Impact of age at diagnosis on long-term prognosis in patients with intestinal Behçet’s disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024;39:519–526. - PubMed
-
- Singh S., Boland B.S., Jess T., Moore A.A. Management of inflammatory bowel diseases in older adults. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2023;8:368–382. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

