A Systematic Review on the Efficacy of Bisphosphonates on Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- PMID: 40698241
- PMCID: PMC12283130
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.86549
A Systematic Review on the Efficacy of Bisphosphonates on Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Abstract
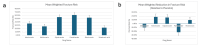
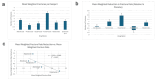
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is a rare genetic disorder that causes frequent fractures. Bisphosphonates play a key role in managing OI. This manuscript examines the comparative effectiveness of alendronate, neridronate, olpadronate, pamidronate, risedronate, and zoledronic acid on fracture rate reduction, increases in lumbar spine (LS) bone mineral density (BMD), and adverse effects compared to placebos and each other. A PubMed search using specific keywords for bisphosphonates and OI yielded 21 sources, from which data about fracture rates, fracture risk, and/or LS BMD were collected. The inclusion criteria consisted of randomized controlled trials involving bisphosphonates to treat OI with data regarding fracture rates, fracture risk, and/or BMD, and the exclusion criteria were any sources that did not meet such standards. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted to assess the significance of differences among bisphosphonates. Neridronate, olpadronate, and risedronate had a lower fracture risk and fracture rate than their placebo counterparts. Olpadronate demonstrated a markedly lower fracture rate compared to its placebo, and neridronate similarly showed a substantially reduced fracture risk relative to its placebo. Risedronate was effective but less so than the other two. Pamidronate showed the largest overall increase in LS BMD, while alendronate demonstrated the highest placebo-adjusted ratio. Despite ANOVA testing finding insignificant differences between drugs, except for fracture risk, limited data constrained the analysis. Adverse effects varied: alendronate caused the most gastrointestinal distress, zoledronic acid and neridronate caused illness-like symptoms, risedronate had illness-like and gastrointestinal symptoms, and pamidronate was linked to severe effects, including death. This analysis highlighted the efficacy and safety profiles of bisphosphonates in the treatment of OI. Neridronate and olpadronate were highly effective in reducing fracture risk and rates, and olpadronate demonstrated superior efficacy in reducing fracture rates. Future research should focus on large, diverse samples, detailed fracture and BMD data, and comparisons across multiple bisphosphonates to refine treatment strategies.
Keywords: bisphosphonate use; bone mineral density; fracture rate; fracture risk; oi osteogenesis imperfecta.
Copyright © 2025, Datir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
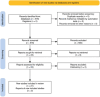

References
-
- Mutation analysis of COL1A1 and COL1A2 in patients diagnosed with osteogenesis imperfecta type I-IV. Pollitt R, McMahon R, Nunn J, Bamford R, Afifi A, Bishop N, Dalton A. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:716. - PubMed
-
- Rodriguez Celin M, Steiner RD, Basel D. GeneReviews® [Internet] Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 2025. COL1A1- and COL1A2-related osteogenesis imperfecta. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
