Complicated traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst: a case report
- PMID: 40698251
- PMCID: PMC12282202
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcr.2025.101221
Complicated traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst: a case report
Abstract
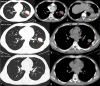
A traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst (TPP) is an uncommon lung lesion that can occur due to blunt chest trauma. This condition is usually harmless and doesn't require medical treatment, but in rare cases, it is complicated by rupture of the lesion and hemothorax. We present the case of a 43-year-old man who fell from a height and suffered chest trauma. Imaging revealed a mass-like lesion and hemothorax, but after ruling out other diagnoses, he was diagnosed with complicated traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst. Over six months, the mass-like lesion shrank and disappeared entirely without any remaining scars. Proper diagnosis and differentiation from other lung lesions are essential in cases of TPP. With conservative management and regular follow-up, the prognosis is generally reasonable.
Keywords: Hemothorax; Lesion; Pulmonary pseudocyst; Trauma.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Severe Relapsing Hailey-Hailey Disease Displaying a Durable Complete Response to Hydroxyurea.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024 Nov;32(3):168-169. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024. PMID: 40654217
-
Large extrapleural hematoma in a patient with Stanford type B acute aortic dissection: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2025 Jul 15;19(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s13256-025-05400-1. J Med Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40665451 Free PMC article.
-
123I-MIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG-PET imaging for diagnosing neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 29;2015(9):CD009263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26417712 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Stopping anticoagulation for isolated or incidental pulmonary embolism: the STOPAPE RCT protocol.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Jun;29(11):1-17. doi: 10.3310/HRCW7937. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 38970429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cho H.J., Jeon Y. Bin, Ma D.S., Lee J.N., Chung M. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocysts after blunt chest trauma: prevalence, mechanisms of injury, and computed tomography findings. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015;79(3):425–430. - PubMed
-
- De Dios J.A., Paoletti L., Bandyopadhyay T. A 27-year-old man with pleuritic chest pain and hemoptysis after a rugby game. Chest. 2009;136(4):1165–1167. - PubMed
-
- Phillips B., Shaw J., Turco L., McDonald D., Carey J., Balters M., et al. Traumatic pulmonary pseudocyst: an underreported entity. Injury. 2017;48(2):214–220. - PubMed
-
- Liu F., Huang Y.C., Ng Y.B., Liang J.H. Differentiate pleural effusion from hemothorax after blunt chest trauma; comparison of computed tomography attenuation values. J Acute Med. 2016;6(1):1–6.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

