Effect of hydrogen carbonate in brewing water on the aroma of tea infusions
- PMID: 40698371
- PMCID: PMC12281027
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102758
Effect of hydrogen carbonate in brewing water on the aroma of tea infusions
Abstract
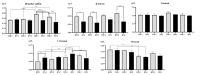
Tea aroma is significantly influenced by hydrogen carbonate (HCO3 -) in brewing water. This study investigated the impact of HCO3 - in water on the aroma of brewed tea infusions using sensory evaluation, headspace solid-phase microextraction, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry techniques. As the concentration of HCO3 - in water increased, the purity of tea aroma diminished, while attributes related to cooked flavors and sweetness intensified; this effect is particularly pronounced at high temperatures and prolonged brewing times. HCO3 - changed the concentration of volatiles, resulting in a significant decrease in concentrations of dimethyl sulfide, β-ionone, and other compounds. Furthermore, the presence of HCO3 - markedly decreased EGCG content while increasing GCG content in tea infusion; these variations in catechin concentrations were correlated with changes in dimethyl sulfide and β-ionone concentrations. These findings enhance the understanding of flavor chemistry concerning tea and water, provide valuable insights for the scientific selection of tea brewing water.
Keywords: Hydrogen carbonate; Tea aroma; Tea brewing water; Water chemistry.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







References
-
- Chen R., Zhang J.A., Fan Z.H. Color and antioxidant change factors of Beijing tap water brewed green tea infusion. Food Science. 2012;33(07):78–82.
-
- Chen S.Y., Xiao Y., Jiang F., Jiang T.N., He X.C., Zhu J.…Zhou Y.M. Effects of water quality factors on the Main components and flavor of cold brew coffee. Science and Technology of Food Industry. 2024;45(05):70–80. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2023050076. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

