Research on RNA modification in disease diagnosis and prognostic biomarkers: current status and challenges
- PMID: 40698864
- PMCID: PMC12284764
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbaf361
Research on RNA modification in disease diagnosis and prognostic biomarkers: current status and challenges
Abstract
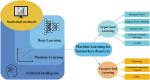
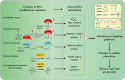
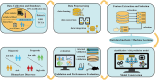
RNA modification, as a crucial post-transcriptional regulatory mechanism, plays a pivotal role in normal physiological processes and is closely associated with the onset and progression of various human diseases. Recent studies have highlighted significant alterations in the level of RNA modifications, including m6A, m6Am, m1A, m5C, m7G, ac4C, Ψ, and A-to-I editing, across multiple diseases. These findings suggest the potential of RNA modifications and their regulatory factors as biomarkers for early disease diagnosis and prognosis. This review provides an overview of statistical methods, machine learning techniques employed in identifying disease diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, along with relevant evaluation metrics and bioinformatics tools. We further explore the types of common RNA modifications, the modifying proteins involved, and the underlying mechanisms of modification. The focus of this paper is on the application of machine learning algorithms in discovering RNA modification-related biomarkers, particularly for disease diagnosis and prognosis. By reviewing recent advancements in the identification of disease biomarkers, and analyzing the prospects and challenges of their clinical application, we aim to offer insights into the mining methods of RNA modifications and their associated factors as disease diagnostic or prognostic biomarkers, providing a valuable reference for future research and clinical practice.
Keywords: RNA modifications; biomarkers; disease diagnosis; machine learning; prognostic models.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RNA modifications in female reproductive physiology and disease: emerging roles and clinical implications.Hum Reprod Update. 2025 Jul 1;31(4):333-360. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmaf005. Hum Reprod Update. 2025. PMID: 40152541 Review.
-
Bioinformatics identification and validation of m6A/m1A/m5C/m7G/ac4 C-modified genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):1055. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14216-7. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40597017 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
RNA modifications in cellular metabolism: implications for metabolism-targeted therapy and immunotherapy.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Mar 27;9(1):70. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01777-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38531882 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

