Is age associated with different vital signs in adults presenting to hospital with bacterial infection? A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40698886
- PMCID: PMC12284760
- DOI: 10.1093/ageing/afaf194
Is age associated with different vital signs in adults presenting to hospital with bacterial infection? A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: It has long been suspected that the vital sign abnormalities that accompany bacterial infection are subtle or absent in older adults. This review summarises the evidence for whether older adults present with different vital sign abnormalities to younger adults when hospitalised with bacterial infection.
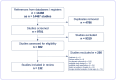
Methods: MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL EBSCO were searched from inception to 19 December 2024 for English-language research articles of patients hospitalised with bacterial infection reporting age and admission vital signs. We used meta-regression to assess how vital signs vary with age. Where studies reported vital signs in multiple age groups, we undertook a meta-analysis in younger (<65) and older patients (≥65). Evidence quality was assessed using an adapted Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 tool.
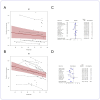
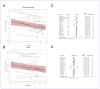
Results: Our search yielded 14 487 studies; 132 were included after screening. Older adults were less likely to be tachycardic (RR 0.82, 0.69 to 0.97, I2 = 86.5%) with a mean difference in heart rate of 5 bpm (-7 to -3 bpm, I2 = 88.3%). Older adults were less likely to be febrile (RR 0.89, 0.83 to 0.95, I2 = 85.9%) with a mean difference in temperature of 0.14°C (-0.26 to -0.02°C, I2 = 94.6%). Most (129/132) studies were at high risk of bias.
Conclusions: Whilst differences in absolute values were small, there was consistency in the finding that older adults were less likely than younger adults to be tachycardic or febrile. As vital signs at presentation may prompt suspicion of infection, influencing investigations and treatment, special consideration for the possibility of infection in older patients with normal vital signs may be warranted.
Keywords: age; diagnosis; infection; older people; systematic review; vital signs.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Geriatrics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
P.W. holds grants from the NIHR and has held grants from Wellcome and Sensyne Health (now Arcturis Data). He was previously Chief Medical Officer for Sensyne Health (now Arcturis Data), holds shares in the company and provides consultancy. He sits on the NIHR HTA General Funding Committee.
Figures

References
-
- Overview of the UK Population: January 2021. Office for National Statistics. https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/populationandmigrati....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

