Inspiratory muscle training for chronic critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 40699051
- PMCID: PMC12266845
- DOI: 10.31744/einstein_journal/2025RW1134
Inspiratory muscle training for chronic critically ill patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Objective: To systematically review and analyze studies investigating the efficacy and safety of inspiratory muscle training in adult chronic critically ill patients.
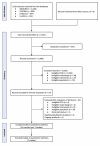
Methods: The MEDLINE, Embase, CENTRAL, LILACS, Clinical Trials Registry, and World Health Organization databases were queried on November 24, 2022 and January 22, 2025. The review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. RevMan V5.4 was used to analyze mean differences or standardized mean differences and 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs) for continuous variables and risk ratios with 95%CIs for dichotomous outcomes. The primary outcomes were inspiratory muscle strength, duration of mechanical ventilation, and severe adverse events; the secondary outcomes were hospital and intensive care unit mortality, intensive care unit and hospital lengths of stay, pulmonary function, non-serious adverse events, respiratory muscle mass, and functional status.
Results: Seven studies (n=390 participants) were included in the analysis. There was a significant increase in inspiratory muscle strength with inspiratory muscle training versus usual care (mean difference, -8.37; 95%CI= -15.21 to -1.52), although the certainty of evidence was very low; when compared with sham interventions, there was no significant difference (mean difference, -4.26; 95%CI= -14.05 to 5.53), also with very low certainty of evidence. The results for pulmonary function, duration of mechanical ventilation, and mortality were imprecise, with very low certainty of evidence. The available evidence also indicates the potential safety benefit of inspiratory muscle training, although the certainty of evidence remains very low. Conclusion: We identified that inspiratory muscle training may improve inspiratory muscle strength, with little to no difference on duration of mechanical ventilation, pulmonary function and severe and non-serious adverse events, when compared to sham inspiratory muscle training and usual care. However, the certainty of the evidence is very low. Evidence regarding the impact of inspiratory muscle training on intensive care unit mortality and length of stay is uncertain. Prospero database registration ID CRD42022370750.
Figures




References
-
- Damuth E, Mitchell JA, Bartock JL, Roberts BW, Trzeciak S. Long-term survival of critically ill patients treated with prolonged mechanical ventilation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3(7):544–553. Review. - PubMed
-
- Carson SS. Definitions and epidemiology of the chronically critically ill. Respir Care. 2012;57(6):848–856. - PubMed
-
- Kandilov A, Ingber M, Morley M, Coomer N, Dalton K, Gage B, et al. Chronically critically ill population payment recommendations (CCIP-PR) RTI International; 2014. [cited 2024 Nov 10]. https://www.cms.gov/priorities/innovation/files/reports/chronicallycriti...
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

