Efficacy and Safety of Biologics for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40699272
- PMCID: PMC12287134
- DOI: 10.1007/s12016-025-09082-x
Efficacy and Safety of Biologics for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
This study aimed to use Bayesian network meta-analysis to compare the efficacy and safety of biologics for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). A comprehensive and systematic search of electronic databases (PubMed, Medline, Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Web of Science, CNKI, and WanFang Data) was conducted from 2014 to September 2024. Our study only included randomized controlled trials with full articles that enrolled adult SLE patients treated with biologics, in comparison with standard therapy. The primary efficacy endpoints were SLE Responder Index 4 (SRI4) and BICLA (BILAG-Based Composite Lupus Assessment). The safety endpoints were adverse events (AEs) and serious adverse events (SAEs). R 4.4.3 and RStudio were used to conduct the network meta-analysis. RevMan 5.4 was used to assess the included literature. 29 randomized controlled trials with a total of 13,712 patients met the inclusion criteria. The network meta-analysis indicated that compared with standard therapy, telitacicept (OR 5.2, 95% CI 1.4-20.0) demonstrated superior efficacy in achieving SRI4 response, deucravacitinib (OR 1.6, 95% CI 1.0-2.5), and anifrolumab (OR 1.6, 95% CI 1.3-2.0) all exhibited significant BICLA response in moderate-to-severe SLE patients. Regarding safety, it was observed that there were no significant statistical differences among the various treatment options. Cluster analysis revealed that deucravacitinib exhibited the best efficacy-safety profile. Deucravacitinib suggested a favorable profile between efficacy and safety. Telitacicept showed the most pronounced improvement in SRI-4 response, but was associated with higher rates of AEs and SAEs, whereas anifrolumab and deucravacitinib displayed advantages in reducing SAEs. For patients with elevated baseline IFN signatures, anti-type I interferon biologics such as anifrolumab and sifalimumab are recommended to maximize clinical benefits. The reliance on indirect comparisons necessitates cautious interpretation of these findings, so further research should prioritize direct head-to-head trials to validate the efficacy and safety profiles of these biologics.
Keywords: Biologics; Network Meta-Analysis; SLE; Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethical Approval: As this is a secondary literature-based study, ethical approval is not necessary. Conflict of interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
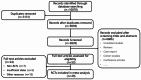
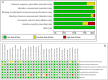
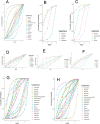
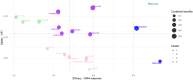


References
-
- Fanouriakis A, Kostopoulou M, Andersen J et al (2024) EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus: 2023 update[J/OL]. Ann Rheum Dis 83(1):15–29. 10.1136/ard-2023-224762 - PubMed
-
- Chen HL, Shen LJ, Hsu PN et al (2018) Cumulative Burden of Glucocorticoid-related Adverse Events in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Findings from a 12-year Longitudinal Study[J/OL]. J Rheumatol 45(1):83–89. 10.3899/jrheum.160214 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- KJ2024CX058/Scientific and Technological Project of Beijing Tongzhou District Plan
- KJ2024CX058/Scientific and Technological Project of Beijing Tongzhou District Plan
- No. 235A2601D/Scientific and Technological Innovation Team Project of Hebei Innovation Capability Enhancement Plan
- No. 235A2601D/Scientific and Technological Innovation Team Project of Hebei Innovation Capability Enhancement Plan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

