Real-World Prophylaxis Outcomes with rIX-FP and rFIXFc for Males with Hemophilia B: Pooled Analysis of Medical Chart Data from Germany and Italy
- PMID: 40699276
- PMCID: PMC12394387
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-025-03303-7
Real-World Prophylaxis Outcomes with rIX-FP and rFIXFc for Males with Hemophilia B: Pooled Analysis of Medical Chart Data from Germany and Italy
Abstract
Introduction: The current standard of care for people with severe hemophilia B is prophylaxis with factor IX (FIX) products. This analysis assessed the effectiveness of prophylaxis for people with hemophilia B (PwHB) receiving rIX-FP or rFIXFc prophylaxis in Germany and Italy.
Methods: A retrospective, de-identified chart review included PwHB ≥ 12 years with severe/moderate hemophilia B from Germany or Italy, receiving prophylaxis with rIX-FP or rFIXFc for ≥ 12 months. The primary outcome was FIX consumption; the secondary outcomes were dosing interval, annualized bleeding rate (ABR), annualized spontaneous bleeding rate (AsBR), and annualized joint bleeding rate (AjBR). These outcomes were also explored in PwHB with pre- and post-rIX-FP switch data.
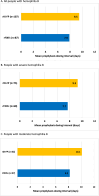
Results: Of 194 PwHB, 107 and 87 received rIX-FP and rFIXFc prophylaxis, respectively. The mean FIX consumption of rIX-FP was significantly lower compared to rFIXFc (42.4 vs. 65.2 IU/kg/week, p = 0.0001), with mean dosing intervals of 9.5 days (rIX-FP) and 7.9 days (rFIXFc). The mean bleeding rates for rIX-FP versus rFIXFc, respectively, were: ABR 0.7 versus 1.1 (p = 0.6704), AsBR 0.1 versus 0.3 (p = 0.3427), and AjBR 0.3 versus 0.4 (p = 0.5296). Subgroup analyses for PwHB with severe and moderate hemophilia B separately showed similar numerical patterns when comparing these outcomes. In the 18 patients with switch data, a significant reduction in FIX consumption was observed (median 51.7 to 33.3 IU/kg/week, p = 0.0069), and the mean dosing interval was extended (7.2-9.5 days). The ABR (median 1.6-0.0, p = 0.0172; n = 18) and AjBR (median 0.6-0.0, p = 0.0200; n = 14) decreased significantly, while the AsBR decreased but not significantly (median 0.2-0.0, p = 0.1460; n = 14).
Conclusion: rIX-FP prophylaxis was associated with reduced FIX consumption versus rFIXFc and offered equally effective or potentially improved bleed protection. Additionally, PwHB who switched to rIX-FP achieved significant decreases in FIX consumption, ABR, and AjBR compared with their prior FIX product.
Keywords: Annualized bleeding rates; Dosing interval; Factor consumption; Hemophilia B; Joint bleeding rates; Prophylaxis; Real world; Spontaneous bleeding rates; rFIXFc; rIX-FP.
Plain language summary
Hemophilia B is a rare inherited bleeding disorder. People with hemophilia are more likely to bleed compared to people without hemophilia; these bleeds can occur either spontaneously or as a result of trauma. People with hemophilia are treated with medication to reduce the risk of bleeds occurring. There are various medications on the market, including coagulation factors. Most of the evidence supporting the use of these medications comes from clinical trials, which are often strictly controlled. Collecting data on the real-world use of medications is also important; however, data comparing different treatments for hemophilia B are currently limited. This study looked at the use of two medications [recombinant factor IX albumin fusion protein (rIX-FP) and recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein (rFIXFc)] commonly used to treat people with hemophilia B in Germany and Italy. Data were collected from medical records of people with hemophilia, including how much medication was received and how often (by intravenous infusion), as well as how many bleeds occurred. The results of this study suggest that the use of one particular medication (rIX-FP) may lead to fewer infusions and reduced product usage, while providing a similar level of bleed control, compared with the other (rFIXFc). For people with hemophilia, reduced infusion frequency decreases treatment burden and, coupled with fewer bleeds, may provide meaningful improvements in the quality of life. This type of real-world study can be useful to provide clinicians with data on how different medications are used in daily clinical practice.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Johannes Oldenburg has received research funding from Bayer, Biotest, CSL Behring, Octapharma, Pfizer, Swedish Orphan Biovitrum and Takeda; consultancy, speakers bureau, honoraria, scientific advisory board and travel expenses from Bayer, Biogen Idec, BioMarin, Biotest, Chugai, CSL Behring, Freeline, Grifols, LFB, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sanofi, Spark Therapeutics, Swedish Orphan Biovitrum and Takeda; Martin Olivieri has received grants/research support from Bayer, Biomarin, Biotest, Takeda, CSL Behring Octapharma, Pfizer, Shire, Roche, Stago and Swedish Orphan Biovitrium, consultancy and speaker fees from Bayer, BioMarin, Biotest, Novo Nordisk, Takeda, CSL Behring, Pfizer, Roche and Swedish Orphan Biovitrium; Songkai Yan, Radovan Tomic, Xiang Zhang and Douglass Drelich are employees of CSL Behring; Ying Yang and Natalie Jakobs are employees of Adivo Associates; Mariasanta Napolitano has acted as consultant for Bayer, Novo Nordisk, Sobi, Kedrion, and has received speaker fees from Takeda, CSL Behring, Bayer, Novo Nordisk, Kedrion, Novartis, Amgen, Sobi, Sanofi Genzyme, Pfizer. Ethics/Ethical approval: Following IRB evaluation, the study was determined to be exempt from IRB oversight as it was secondary research using non-identifiable information for which informed consent is not required.
Figures
References
-
- Srivastava A, Santagostino E, Dougall A, Kitchen S, Sutherland M, Pipe SW, et al. WFH Guidelines for the management of hemophilia, 3rd edition. Haemophilia. 2020;26(Suppl 6):1–158. - PubMed
-
- Castaman G. The benefits of prophylaxis in patients with hemophilia B. Expert Rev Hematol. 2018;11(8):673–83. - PubMed
-
- Metzner HJ, Weimer T, Kronthaler U, Lang W, Schulte S. Genetic fusion to albumin improves the pharmacokinetic properties of factor IX. Thromb Haemost. 2009;102(4):634–44. - PubMed
-
- Powell JS, Pasi KJ, Ragni MV, Ozelo MC, Valentino LA, Mahlangu JN, et al. Phase 3 study of recombinant factor IX Fc fusion protein in hemophilia B. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(24):2313–23. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical