Association of white matter injury and neuroinflammation in the post-acute phase after ischemic stroke using [18F]FEPPA-PET/MRI
- PMID: 40699407
- PMCID: PMC12287493
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-025-01288-6
Association of white matter injury and neuroinflammation in the post-acute phase after ischemic stroke using [18F]FEPPA-PET/MRI
Abstract
Background: Cerebral white matter (WM) injury after ischemic stroke is associated with post-stroke cognitive impairment (PSCI), however, the interaction between sustained neuroinflammation and post-stroke WM injury is not well understood. Hybrid PET/MRI can provide insight into pathophysiological mechanisms linking chronic neuroinflammation, ischemic WM injury, and PSCI. Using PET/MRI, this study investigated the relationship between [18F]FEPPA standardized uptake value ratio (SUVr) measurements of glial activation and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) measurements of microstructure integrity in brain WM regions in the chronic phase at 6-months after acute ischemic stroke.
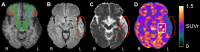
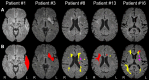
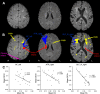
Results: [18F]FEPPA-PET, DTI, and T2-weighted FLAIR were acquired at 6-months post-stroke in 19 elderly humans (seven females; mean age = 76 ± 5 years) with confirmed first-ever acute ischemic stroke using hybrid PET/3T-MRI. Index infarcts, chronic (incidental, covert) infarcts, and WM hyperintensities were manually segmented on FLAIR and excluded from the imaging analysis. Pearson correlation was conducted to assess the association between [18F]FEPPA-SUVr and DTI measurements in WM regions commonly implicated in PSCI. [18F]FEPPA-SUVr was elevated in brain regions ipsilateral to the index infarct at 6-months post-stroke, and these increases correlated with decreases in fractional anisotropy in several WM pathways linked to PSCI, including right superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) III (r = -0.82, p < 0.0001), right anterior thalamic radiation (r = -0.61, p = 0.006), and right arcuate fasciculus (r = -0.56, p = 0.01). Elevated [18F]FEPPA-SUVr was also associated with increased mean diffusivity (r = 0.69, p < 0.001), axial diffusivity (r = 0.55, p = 0.02), and radial diffusivity (r = 0.74, p < 0.001) in right SLF III.
Conclusions: This study found an association between elevated post-acute glial activation (neuroinflammation) and reduced microstructure integrity in brain WM pathways ipsilateral to ischemic infarcts and remote from WM lesions at 6-months post-stroke. Hybrid PET/MRI is promising to be a valuable tool for probing post-acute neuroinflammation and associated changes in cerebral WM pathways following ischemic stroke.
Keywords: Diffusion tensor imaging; Neuroinflammation; PET/MRI; Stroke; White matter; [18F]FEPPA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The study was approved by the Western University Research Ethics Board and conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki ethical standards. All patients provided written informed consent to participate. Consent for publication: All patients gave written consent for publication. Competing interests: All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of Central Arterial Stiffness With Brain White Matter Integrity and Gray Matter Volume in MRI Across the Adult Lifespan.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Jul;62(1):215-229. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29713. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39792583 Free PMC article.
-
MRI Assessment of Geometric Microstructural Changes of White Matter in Infants With Periventricular White Matter Injury and Spastic Cerebral Palsy.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Aug;62(2):403-414. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29730. Epub 2025 Feb 7. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39917817
-
Plasma Oligomer β-Amyloid and White Matter Microstructural Integrity in Cognitively Normal Older Adults According to Cerebral Amyloid Deposition.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023;10(4):837-846. doi: 10.14283/jpad.2023.87. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2023. PMID: 37874106
-
123I-MIBG scintigraphy and 18F-FDG-PET imaging for diagnosing neuroblastoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 29;2015(9):CD009263. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009263.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26417712 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of fractional anisotropy in preterm-born individuals: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024 Dec;44(1):2371956. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2024.2371956. Epub 2024 Jul 10. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2024. PMID: 38984803
References
-
- Thiel A, Vahdat S. Structural and resting-state brain connectivity of motor networks after stroke. Stroke. 2015;46:296–301. - PubMed
-
- de Groot M, Verhaaren BFJ, de Boer R, Klein S, Hofman A, van der Lugt A, et al. Changes in normal-appearing white matter precede development of white matter lesions. Stroke. 2013;44:1037–42. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada/Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada
- Lawson Health Research Institute/Lawson Health Research Institute
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- Canadian Institutes of Health Research/CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- Max-Planck-Gesellschaft/Max-Planck-Gesellschaft
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

