Nature-based interventions for enhancing resilience in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40699470
- PMCID: PMC12287494
- DOI: 10.1007/s44192-025-00258-7
Nature-based interventions for enhancing resilience in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
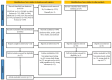
Despite increasing interest in nature-based interventions (NBIs) for mental health, no or very few prior reviews have quantitatively synthesised their effects on children's resilience, a key developmental outcome. This study systematically reviews and meta-analyses available evidence following PRISMA guideline. The Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature, Cochrane, Embase, Education Resources Information Center, Medline, APA PsycArticles, SPORTDiscus, and Web of Science were searched from inception to November 28, 2024. For additional studies, Google Scholar and references from included studies were searched. The review included randomised clinical trials, controlled trials, and single-group pre-post studies reporting resilience. Findings not synthesised quantitatively were summarised narratively. A total of 13 articles involved 15 studies with 2,571 participants (mean age 15.57 years; range 13 to 17 years; 1315 [53%] female). Random-effect meta-analysis indicated significant moderate-to-large short-term effects of NBIs on children's resilience (standardised mean difference, 0.64; 95% confidence level, 0.36 to 0.91; p <.001). Substantial heterogeneity of intervention effects was observed (I2 = 98%). This review provides preliminary evidence that NBIs may be associated with short-term improvements in resilience among children, though results should be interpreted cautiously due to study limitations. This early evidence highlights a community-based approach that may support resilience development through nature. Sailing showed some promise as an early observation noted in subgroup analysis and narrative synthesis emphasising nature-human kinship. High-quality trials are needed to evaluate the effects of sailing on resilience and address gaps: the long-term effect of NBIs and their impact on children outside the 13-17 age range. Trail registration: PROSPERO database (CRD42025634371).
Keywords: Children; Mental health; Nature-based interventions; Resilience.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Falls prevention interventions for community-dwelling older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis of benefits, harms, and patient values and preferences.Syst Rev. 2024 Nov 26;13(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s13643-024-02681-3. Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39593159 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Educational interventions for the management of cancer-related fatigue in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Nov 24;11(11):CD008144. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008144.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27883365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stoltz PG. Adversity quotient: turning obstacles into opportunities. John Wiley & Sons; 1999.
-
- Brewer-Smyth K. Adverse childhood experiences: the neuroscience of trauma, resilience and healing throughout the life course. Springer Nature; 2022.
-
- Leung DY, Chan AC, Ho GW. Resilience of emerging adults after adverse childhood experiences: a qualitative systematic review. Trauma Violence Abuse. 2022;23(1):163–81. - PubMed
-
- Avdagic E, Wade C, McDonald M, McCormack D, Dakin P, Macvean M, Hayes L, Phan T. Resilience in young children: a delphi study to reach consensus on definitions, measurement and interventions to build resilience. Early Child Dev Care. 2020;190(13):2066–77.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources