Orthobiologics Revisited: A Concise Perspective on Regenerative Orthopedics
- PMID: 40699646
- PMCID: PMC12025442
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47040247
Orthobiologics Revisited: A Concise Perspective on Regenerative Orthopedics
Abstract
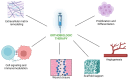
At the forefront of regenerative medicine, orthobiologics represent a spectrum of biological substances that offer promising alternatives for tissue repair and regeneration. Traditional surgical treatments often involve significant risks, extended recovery periods, and may not fully restore tissue functionality, creating a strong demand for less invasive options. This paper presents a concise overview of orthobiologics, reexamining their role within the broader landscape of regenerative medicine. Beginning with a brief introduction to orthobiologics, the paper navigates through various types of biological materials and their associated mechanisms of action and clinical applications. By highlighting platelet derivatives, bone marrow-derived products, and processed adipose tissue, among others, it underscores the pivotal role of orthobiologics in prompting biological responses like cellular proliferation, differentiation, and angiogenesis, thereby fostering tissue healing. Furthermore, this paper explores the diverse applications of orthobiologics in orthopedic conditions, outlining their utility in the treatment of bone and soft-tissue injuries. Addressing clinical considerations, it discusses safety profiles, efficacy, patient selection criteria, and emerging challenges. With the limitations of traditional medicine becoming more apparent, orthobiologics offer an innovative and less invasive approach to patient care. Looking forward, this paper approaches future directions in orthobiologics research, emphasizing the need for continued innovation and exploration. Through a concise perspective, this paper aims to provide clinicians, researchers, and stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of orthobiologics and their evolving role in regenerative medicine.
Keywords: growth factors; orthobiologics; regenerative medicine; stem cells; tissue regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Costa F.R., Costa Marques M.R., Costa V.C., Santos G.S., Martins R.A., Santos M.d.S., Santana M.H.A., Nallakumarasamy A., Jeyaraman M., Lana J.V.B., et al. Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid in Osteoarthritis and Tendinopathies: Molecular and Clinical Approaches. Biomedicines. 2023;11:1061. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041061. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources