As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells
- PMID: 40699652
- PMCID: PMC12025865
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47040253
As2S2 Mediates the ROS/P38 MAPK Signaling Pathway to Induce Apoptosis and S-Phase Arrest in Myelodysplastic Syndrome Cells
Abstract
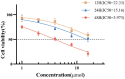
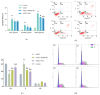
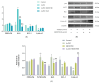
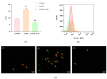
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) is a heterogeneous myeloid clonal disorder that represents a significant threat to human health. As2S2, a natural compound, has been shown to exert therapeutic effects on various malignant tumors, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), breast cancer, and osteosarcoma, based on extensive clinical experience. In this study, we investigated the mechanism by which As2S2 inhibits the proliferation of the myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) SKM-1 cell line. Our findings revealed that As2S2 inhibited the proliferation of SKM-1 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Flow cytometry, protein immunoblotting, and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR analyses demonstrated that As2S2 promotes the phosphorylation of P38 MAPK, thereby activating the MAPK signaling pathway. Additionally, it promotes apoptosis by increasing the BAX/Bcl-2 ratio and induces S-phase arrest through the downregulation of the cell cycle-related protein cyclin A2. Further studies demonstrated that As2S2-treated cells exhibited ROS accumulation under fluorescence microscopy, along with activation of the P38 MAPK signaling pathway, increased apoptosis, and S-phase arrest in the cell cycle. This process could be partially reversed by the ROS inhibitor N-acetylcysteine. Therefore, the results of the present study suggest that As2S2 induces ROS accumulation in SKM-1 cells, which contributes to the activation of the P38 MAPK signaling pathway, promoting apoptosis and S-phase arrest in the cell cycle. Additionally, As2S2 may serve as a potent therapeutic agent for the treatment of myelodysplastic syndromes, with ROS acting as one of the key therapeutic targets.
Keywords: As2S2; P38 MAPK; ROS; apoptosis; myelodysplastic syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Thrombopoietin mimetics for patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Sep 30;9(9):CD009883. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009883.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28962071 Free PMC article.
-
M1 Macrophage-Derived TNF-α Promotes Pancreatic Cancer Ferroptosis Via p38 MAPK-ACSL4 Pathway.Curr Mol Med. 2025 Jul 10. doi: 10.2174/0115665240374551250630075409. Online ahead of print. Curr Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40653839
-
Ellipticine targets FGFR3 to mediate the RAS/MAPK-P38 signalling pathway to induce apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.3 Biotech. 2025 May;15(5):111. doi: 10.1007/s13205-025-04269-7. Epub 2025 Apr 3. 3 Biotech. 2025. PMID: 40191451
-
Cinobufagin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human osteosarcoma U2OS cells through the ROS/JNK/p38 signaling pathway.Oncol Rep. 2016 Jul;36(1):90-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.4782. Epub 2016 Apr 28. Oncol Rep. 2016. Retraction in: Oncol Rep. 2025 Aug;54(2):95. doi: 10.3892/or.2025.8928. PMID: 27176794 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
p38 MAPK signaling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease pathogenesis and inhibitor therapeutics.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Nov 2;21(1):314. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01337-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 37919729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arber D.A., Orazi A., Hasserjian R., Thiele J., Borowitz M.J., Le Beau M.M., Bloomfield C.D., Cazzola M., Vardiman J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2016;127:2391–2405. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hu X.-M., Yuan B., Tanaka S., Song M.-M., Onda K., Tohyama K., Zhou A.-X., Toyoda H., Hirano T. Arsenic disulfide-triggered apoptosis and erythroid differentiation in myelodysplastic syndrome and acute myeloid leukemia cell lines. Hematology. 2013;19:352–360. doi: 10.1179/1607845413y.0000000138. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

