The Inflammatory Link of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Thrombosis: Pathogenic Molecular Circuits and Treatment Approaches
- PMID: 40699690
- PMCID: PMC12025962
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47040291
The Inflammatory Link of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Thrombosis: Pathogenic Molecular Circuits and Treatment Approaches
Abstract
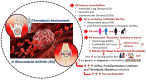
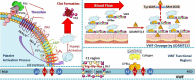
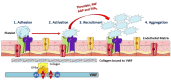
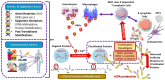
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by systemic inflammation that primarily affects the joints but can also involve extra-articular organs. Its multifactorial etiology remains incompletely understood, necessitating further investigation into its underlying mechanisms. The primary therapeutic goal in RA management is to achieve disease remission or maintain low RA activity to prevent long-term morbidity. RA therapies aim to mitigate joint damage, reduce disability, and prevent systemic complications such as cardiovascular diseases. In addition to pharmacological treatments, non-pharmacological interventions-including physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and lifestyle modifications such as smoking cessation, regular exercise, and adherence to a balanced diet-play a crucial role in managing the disease. Beyond joint inflammation, RA has been strongly associated with an increased risk of thrombosis, contributing significantly to both morbidity and mortality. The link between RA and thrombotic events arises from a complex interplay of inflammatory pathways, endothelial dysfunction, and coagulation abnormalities. This review provides an in-depth analysis of the mechanisms driving the association between thrombo-inflammatory manifestations and the incidence of RA, the impact of RA treatment on thrombosis prevalence, and potential therapeutic strategies for managing both conditions concurrently. By integrating recent advancements in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) pathophysiology and thrombo-inflammatory research, this paper provides a comprehensive resource on the inflammatory link between RA and thrombosis while discussing and comparing current and emerging treatment approaches. Further investigation into these mechanisms could facilitate the development of targeted therapies that reduce the risk of thrombosis in patients with RA.
Keywords: DMARDs; anti-rheumatic drugs; anticoagulants; antithrombotic therapy; autoimmune diseases; inflammation; rheumatoid arthritis; thrombosis; venous thromboembolic events.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Fernandez-Gonzalez M., Fernandez-Lao C., Martin-Martin L., Gonzalez-Santos A., Lopez-Garzon M., Ortiz-Comino L., Lozano-Lozano M. Therapeutic Benefits of Balneotherapy on Quality of Life of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021;18:13216. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182413216. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

