CRISPR-Cas9 in the Tailoring of Genetically Engineered Animals
- PMID: 40699729
- PMCID: PMC12109904
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47050330
CRISPR-Cas9 in the Tailoring of Genetically Engineered Animals
Abstract
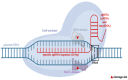
CRISPR-Cas9 enables targeted genome editing and has become a pivotal tool in biomedical research and animal genome engineering. This review highlights its application in generating genetically modified animals used as preclinical disease models, bioreactors for recombinant protein production, and potential sources of xenotransplantation organs. We also discuss its role in improving livestock traits, welfare, and breeding efficiency. The benefits and limitations of CRISPR-Cas9 are examined, emphasizing its transformative potential in research and agricultural biotechnology.
Keywords: CRISPR-Cas9; genetically engineered animals; genome editing; model organisms; xenotransplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advancing crop disease resistance through genome editing: a promising approach for enhancing agricultural production.Front Genome Ed. 2024 Jun 26;6:1399051. doi: 10.3389/fgeed.2024.1399051. eCollection 2024. Front Genome Ed. 2024. PMID: 38988891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on molecular scissoring with CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing technology.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024 Jul 12;13(4):tfae105. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfae105. eCollection 2024 Aug. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2024. PMID: 39006883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in Ganoderma lucidum: recent advances and biotechnological opportunities.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 25;41(7):223. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04458-9. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40560492 Review.
-
Transferable approaches to CRISPR-Cas9 induced genome editing in non-model insects: a brief guide.Front Zool. 2025 Jul 7;22(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12983-025-00566-2. Front Zool. 2025. PMID: 40624545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Off-target interactions in the CRISPR-Cas9 Machinery: mechanisms and outcomes.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Jul 5;43:102134. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102134. eCollection 2025 Sep. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40688512 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ishino Y., Shinagawa H., Makino K., Amemura M., Nakata A. Nucleotide Sequence of the Iap Gene, Responsible for Alkaline Phosphatase Isozyme Conversion in Escherichia Coli, and Identification of the Gene Product. J. Bacteriol. 1987;169:5429–5433. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5429-5433.1987. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

