The N-Linked Glycosylation Site N201 in eel Lutropin/Choriogonadotropin Receptor Is Uniquely Indispensable for cAMP Responsiveness and Receptor Surface Loss, but Not pERK1/2 Activity
- PMID: 40699744
- PMCID: PMC12110046
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47050345
The N-Linked Glycosylation Site N201 in eel Lutropin/Choriogonadotropin Receptor Is Uniquely Indispensable for cAMP Responsiveness and Receptor Surface Loss, but Not pERK1/2 Activity
Abstract
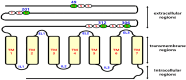
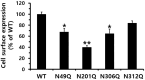
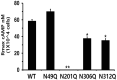
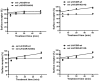
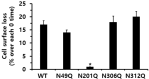
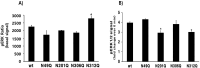
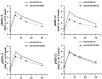
The seven transmembrane-spanning lutropin/chorionic gonadotropin receptors (LH/CGRs) trigger extracellular signal-related kinases (ERK1/2) via a noticeable network dependent on either G protein (Gαs) or β-arrestins. LH/CGRs are highly conserved, with the largest region within the transmembrane helices and common N-glycosylation sites in the extracellular domain. We aimed to determine the glycosylation sites that play crucial roles in cAMP and pERK1/2 regulation by constructing four mutants (N49Q, N201Q, N306Q, and N312Q). The cAMP response in cells expressing the N201Q mutant was completely impaired, despite high-dose agonist treatment. The cell-surface expression level was lowest in transiently transfected cells, but normal surface loss of the receptor occurred in cells expressing the wild-type and other mutant proteins. However, the N201Q mutant was only slightly reduced after 5 min of agonist stimulation. All mutants showed a peak in cAMP signaling 5 min after stimulation with a pERK1/2 agonist. Of note, cAMP activity was completely impaired in the N201Q mutant; however, this mutant still displayed a pERK1/2 response. These data show that the specific N-linked glycosylation site in eel LH/CGR is clearly distinguished by its differential responsiveness to cAMP signaling and pERK1/2 activity. Thus, we suggest that the cAMP and pERK1/2 signaling pathways involving eel LH/CGRs represent pleiotropic signal transduction induced by agonist treatment.
Keywords: N-linked glycosylation; cAMP responsive; eel LH/CGR; pERK1/2 activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kara E., Crepieux P., Gauthier C., Martinat N., Piketty V., Guillou F., Reiter E. A phosphorylation cluster of five serine and threonine residues in the C-terminus of the follicle-stimulating hormone receptor is important for desensitization but not for β-arrestin-mediated ERK activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006;20:3014–3026. doi: 10.1210/me.2006-0098. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

