Differential Profiles of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites of Bile Acids and Propionate as Potential Predictors of Depressive Disorder in Women with Morbid Obesity at High Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-A Pilot Study
- PMID: 40699752
- PMCID: PMC12110740
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47050353
Differential Profiles of Gut Microbiota-Derived Metabolites of Bile Acids and Propionate as Potential Predictors of Depressive Disorder in Women with Morbid Obesity at High Risk of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-A Pilot Study
Abstract
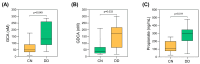
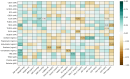
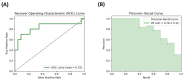
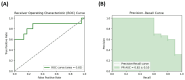
Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) is a liver condition linked to cardiometabolic diseases and mental health issues, with studies highlighting disruptions in gut microbiota activity, including bile acid (BA) metabolism. Therefore, the main aim of this exploratory analysis was to assess microbiota-derived metabolites, specifically BAs and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), as potential biomarkers of depressive disorder (DD) in women with morbid obesity at MASLD risk. In this pilot study, 33 females with morbid obesity who were scheduled for bariatric surgery were evaluated. Medical and clinical data were collected, and microbial metabolites from pre-surgery blood samples were analyzed. Patients were stratified according to the presence of DD. Analysis with Spearman's rank test was used to assess correlations and logistic regression models were built to evaluate biomarkers as predictors of DD risk using both receiver operating characteristic (ROC) and precision-recall curves. In this cohort, 30.3% of females were reported to have DD, in addition to significantly elevated levels of certain BAs and SCFAs, including glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) and propionate, which were also correlated with some metabolic biomarkers. However, there were no differences in the incidence of MASLD or metabolic syndrome between patients with DD or without. In conclusion, microbiota-derived metabolites such as GDCA and propionate may influence DD risk in females with morbid obesity; however, their potential use as predictive biomarkers should be further investigated to confirm their role in psycho-metabolic conditions.
Keywords: bile acids; depression; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; microbial metabolites; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Gut microbiome-based interventions for the management of obesity in children and adolescents aged up to 19 years.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jul 10;7(7):CD015875. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015875. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40637175 Review.
-
Higher Pre-Operative Non-Invasive Fibrosis Scores are not Associated with Surgical Outcomes in Patients with MASLD Undergoing Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.Can Liver J. 2025 Feb 12;8(2):284-289. doi: 10.3138/canlivj-2024-0015. eCollection 2025 May. Can Liver J. 2025. PMID: 40677984 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic treatments for metastatic cutaneous melanoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Feb 6;2(2):CD011123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29405038 Free PMC article.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
-
The Significance of the Presence of Gilbert's Syndrome in Patients With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A Retrospective Cohort Study.Cureus. 2025 May 30;17(5):e85074. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85074. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40585738 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xiao J., Lim L.K.E., Ng C.H., Tan D.J.H., Lim W.H., Ho C.S.H., Tan E.X.X., Sanyal A.J., Muthiah M.D. Is Fatty Liver Associated With Depression? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review on the Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Depression and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Med. 2021;8:691696. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.691696. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

