Synergistic Antitumor Effects of Ivermectin and Metformin in Canine Breast Cancer via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibition
- PMID: 40699802
- PMCID: PMC12191936
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47060403
Synergistic Antitumor Effects of Ivermectin and Metformin in Canine Breast Cancer via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway Inhibition
Abstract
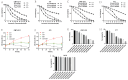
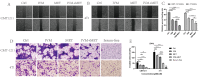
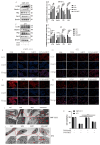
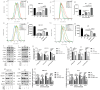
Ivermectin (IVM) is a macrolide antiparasitic drug, and Metformin (MET) is a biguanide oral hypoglycemic drug. Studies have shown that both of them have obvious anti-tumor effects, but there have been no reports on the combined treatment of Canine breast tumors. This report aimed to investigate the effectiveness and the possible mechanism of drug combination on Canine breast cancers. Mouse breast tumor cells (4T1) and canine breast tumor cells (CMT-1211) were, respectively, treated with IVM, MET, and their combination, and then cell viability was assessed. After that, transcriptomic analysis was performed to study the action pathway of the drug combination with regard to its anti-tumor effects. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels were detected by flow cytometry, and autophagosome formation was observed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Immunofluorescence detected the cytoplasmic translocation of LC3B and P62 into the nucleus. Western blot detected the protein expressions of LC3B, P62, Beclin1, Bcl-2, p-PI3K, p-AKT, and p-mTOR. Our transcriptomic analysis showed that the combination of IVM and MET regulated the expression of autophagy-related genes and pathways, including the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Our in vitro experiments showed that the combination of two drugs had a considerably significant effect on cytotoxicity, ROS levels, and the formation of autophagosomes compared to each drug alone. Meanwhile, the in vivo experiments showed that IVM combined with MET had an obvious inhibitory effect on tumor growth in canine breast tumor xenografts. This study concluded that IVM with MET activated autophagy, which killed breast cancer cells by inhibiting the activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and promoting the excessive accumulation of ROS. It offers a theoretical foundation for the synergistic effects of MET and IVM to suppress breast cancer cell activity.
Keywords: PI3K/AKT/mTOR; ROS; autophagy; ivermectin; metformin.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors read and approved of this article in its present form. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Wheat-grain moxibustion combined with chemotherapy inhibits tumor growth by suppressing PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer mice].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jul 25;50(7):790-798. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20240438. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40691029 Chinese.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-210 Regulates Autophagy Through the AMPK/mTOR Signaling Pathway, Reduces Neuronal Cell Death and Inflammatory Responses, and Enhances Functional Recovery Following Cerebral Hemorrhage in Mice.Neurochem Res. 2025 Jun 5;50(3):180. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04434-7. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40471451 Free PMC article.
-
[Electroacupuncture of "Jiaji"(EX-B2) improves asthma by reducing airway inflammation and regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in rats with allergic asthma].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025 Jun 25;50(6):666-674. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20241336. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2025. PMID: 40551649 Chinese.
-
[Volume and health outcomes: evidence from systematic reviews and from evaluation of Italian hospital data].Epidemiol Prev. 2013 Mar-Jun;37(2-3 Suppl 2):1-100. Epidemiol Prev. 2013. PMID: 23851286 Italian.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

