Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 40699811
- PMCID: PMC12191647
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47060412
Novel Thymoquinone Derivative TQFL28 Inhibits Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) Invasiveness In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
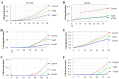
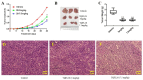
Although thymoquinone (TQ) has been reported as an anti-tumor small molecule well investigated in numerous tumors. In this study, we designed and synthesized a novel TQ derivative, TQFL28, with a molecular formula of C20H23NO2. TQFL28 showed stronger cytotoxicity or anti-proliferative activities against triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell lines (BT549, MDA-MB-231, or 4T1) than TQ but is lower in the normal mammary epithelial cells, MCF10A. TQFL28 exhibited lower IC50 values toward BT549 (38.78 ± 1.589) and MDA-MB-231 (39.63 ± 1.598) cells compared to TQ, indicating its efficacy for TNBC cytotoxicity. TQFL28 inhibited the growth, migration, and invasiveness of TNBC cells of 4T1 and BT549 in vitro and tumor progression and metastasis in a 4T1 allograft animal model in vivo. Moreover, TQFL28 presents lower toxicity than TQ in mice, showing a 7-day half-lethal dose (LD50) of 59.43 mg/kg (41.6-83.6, 95% confidence interval). Altogether, our study obtained. In addition, TQFL28 induced a significant reduction in tumor volumes in the mouse model in comparison to the vehicle group. TQFL28, a novel small molecule, has a superior inhibitory effect and lower toxicity on TNBC both in vitro and in vivo. Thus, TQFL28 might have potential as a therapeutic small molecule for breast cancer, especially in TNBC.
Keywords: TQFL28; anti-cancer; derivative; invasiveness; thymoquinone; triple-negative breast cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TQFL13, a novel synthetic derivative of thymoquinone (TQ), is more capable of inhibiting breast cancer progression than TQ.Bioorg Chem. 2025 Aug 6;164:108837. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108837. Online ahead of print. Bioorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 40774107
-
Tumor therapy by targeting extracellular hydroxyapatite using novel drugs: A paradigm shift.Cancer Med. 2024 Feb;13(3):e6812. doi: 10.1002/cam4.6812. Epub 2024 Jan 18. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 38239047 Free PMC article.
-
Sulindac modulates the response of triple negative breast cancer to anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 17:2025.06.11.659159. doi: 10.1101/2025.06.11.659159. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40666926 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheng J., Song B., Wei C., Zhang L., Liu X., Yang L., Tima S., Chiampanichayakul S., Xiao X., Anuchapreeda S., et al. Exploring breast cancer associated-gene panel for next-generation sequencing and identifying new, pathogenic variants in breast cancer from western China. J. Cancer. 2025;16:1281–1295. doi: 10.7150/jca.101911. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

