Pharmaco-nutraceutical improvement of the response to obeticholic acid with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
- PMID: 40699986
- PMCID: PMC12493161
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20253113
Pharmaco-nutraceutical improvement of the response to obeticholic acid with omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Abstract
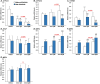
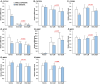
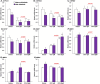
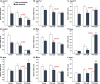
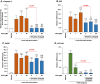
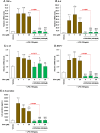
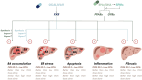
Obeticholic acid (OCA) is the second-line therapy for primary biliary cholangitis. While efficient in promoting bile acid (BA) detoxification and limiting liver fibrosis, its clinical use is restricted by severe dose-dependent side effects. We tested the hypothesis that adding n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), eicosapentaenoic (EPA) and docosahexaenoic (DHA) acids to OCA may improve the therapeutic effect of the low drug dosage. Several liver cell lines were exposed to vehicle, low or high OCA dose (1-20 μM) in the presence or absence of EPA/DHA for 24 h. To induce ER stress, apoptosis, and fibrosis, HepG2 cells were exposed to a 400 μM BA mixture or to 2 ng/ml transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β). For inflammation analyses, THP-1 cells were activated with 100 ng/ml lipopolysaccharides (LPS). The impact of OCA+EPA/DHA was assessed using transcriptomic (qRT-PCR), proteomic (ELISA, caspase-3), and metabolomic (LC-MS/MS) approaches. The addition of EPA/DHA reinforced the ability of low OCA dose to down-regulate the expression of genes involved in BA synthesis (CYP7A1 and CYP8B1) and uptake (NTCP) and to up-regulate the expression of MRP2 and 3 genes. EPA/DHA also enhanced the anti-inflammatory response of the drug by reducing the expression of the LPS-induced cytokines: tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in THP-1 macrophages. OCA+EPA/DHA decreased the expression of BIP, CHOP, and COL1A1 genes and the caspase-3 activity. EPA+DHA potentiate the response to low OCA doses on BA toxicity and provide additional benefits on ER stress, apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis. These observations support the idea that adding n-3 PUFAs to the drug may reduce the risk of dose-related side effects in patients treated with OCA.
Keywords: autoimmune liver diseases; bile acid detoxification; drug response improvement; inflammation and fibrosis resolution; n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Professor Barbier is founder, shareholder and member of the board of directors of Trienix Pharma Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Krupa K.N., Nguyen H., Parmar M. Obeticholic Acid StatPearls. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567735/ - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

