RNA-programmable cell-type monitoring and manipulation in the human cortex with CellREADR
- PMID: 40700016
- PMCID: PMC12414115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116037
RNA-programmable cell-type monitoring and manipulation in the human cortex with CellREADR
Abstract
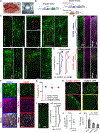
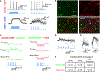
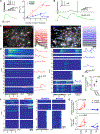
Reliable and systematic access to diverse cell types is necessary for understanding the organization, function, and pathophysiology of human neural circuits. Methods for targeting human neural populations are scarce and currently center on identifying transcriptional enhancers and engineering viral capsids. Here, we demonstrate the utility of cell access through RNA sensing by endogenous adenosine deaminase acting on RNA (ADAR) (CellREADR), a programmable RNA sensor-effector technology that couples cellular RNA sensing to effector protein translation, for accessing, monitoring, and manipulating specific neuron types in the human cortex ex vivo. We design CellREADRs to target two subpopulations-calretinin (CALB2) GABAergic interneurons and forkhead box protein P2 (FOXP2) glutamatergic projection neurons-and then validate targeting specificity using histological, electrophysiological, and transcriptomic methods. CellREADR expression of channelrhodopsin and GCamp enables the manipulation and monitoring of these populations in live cortical microcircuits. By demonstrating specific, reliable, and programmable experimental access to human neuronal subpopulations, our results highlight CellREADR's potential for studying neural circuits and treating brain disorders.
Keywords: CP: Molecular biology; CP: Neuroscience; PatchSeq; RNA sensor; calcium imaging; cellular access; cortex; excitatory neuron; human neuroscience; interneuron; optogenetics; organotypic slice culture.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests Z.J.H. has filed patents for CellREADR (US patent nos. PCT/US22/79004 and PCT/US22/7900). Z.J.H. is a co-founder of Doppler Bio.
Figures


Update of
-
RNA-programmable cell type monitoring and manipulation in the human cortex with CellREADR.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 9:2024.12.03.626590. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.03.626590. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cell Rep. 2025 Aug 26;44(8):116037. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116037. PMID: 39677799 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Zeng H, and Sanes JR (2017). Neuronal cell-type classification: challenges, opportunities and the path forward. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 530–546. - PubMed
-
- Siletti K, Hodge R, Mossi Albiach A, Lee KW, Ding S-L, Hu L, Lönnerberg P, Bakken T, Casper T, Clark M, et al. (2023). Transcriptomic diversity of cell types across the adult human brain. Science 382, eadd7046. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

