Effects of Pulsed Radiofrequency Current and Thermal Condition on the Expression of β-Endorphin in Human Monocytic Cells
- PMID: 40700132
- PMCID: PMC12285971
- DOI: 10.3390/neurosci6030067
Effects of Pulsed Radiofrequency Current and Thermal Condition on the Expression of β-Endorphin in Human Monocytic Cells
Abstract
Pulsed radiofrequency (PRF) current applied to peripheral nerves is a modality used in interventional pain medicine, but its underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate whether ex vivo exposure of human monocytic THP-1 cells to PRF current or to heat induces β-endorphin production.
Methods: THP-1 cells were exposed to PRF current for 15 min or incubated at elevated temperatures (42 °C to 50 °C) for 3 or 15 min. Flow cytometry was used to assess cell viability, and β-endorphin concentrations in culture supernatants were quantified by ELISA. In a separate experiment, cells were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to compare its effects on β-endorphin release.
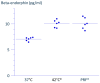
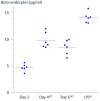
Results: A 3 min exposure to temperatures ≥ 46 °C reduced THP-1 cell viability, whereas a 15 min exposure to PRF current or to heat at 42 °C did not impair viability. Both PRF current and mild heat significantly enhanced β-endorphin release. β-Endorphin levels in the supernatant of LPS-stimulated cells were comparable to those of cells exposed to PRF current.
Conclusions: Ex vivo application of PRF current or mild heat enhanced β-endorphin production from THP-1 cells without significant cytotoxicity. These preliminary findings warrant further investigation using primary human monocytes and in vivo models to assess therapeutic potential.
Keywords: THP-1 cells; apoptosis; beta-endorphin; monocytes; neuropathic pain; proopiomelanocortin (POMC); pulsed radiofrequency current; thermal effect.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pulsed radiofrequency of lumbar dorsal root ganglion for lumbar radicular pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pain Pract. 2024 Jun;24(5):772-785. doi: 10.1111/papr.13351. Epub 2024 Jan 31. Pain Pract. 2024. PMID: 38294072
-
Efficacy of horizontal platelet-rich fibrin on gingival tissue regeneration: Cellular and histological analysis.J Periodontol. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1002/jper.11364. Online ahead of print. J Periodontol. 2025. PMID: 40577439
-
Comparison of Two Different Neuromodulation Treatments in Patients With Acute Zoster-Related Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain and Pain Catastrophizing.Neuromodulation. 2025 Jun;28(4):567-574. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2025.01.010. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Neuromodulation. 2025. PMID: 39955663 Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of combining pulsed radiofrequency with low-temperature continuous radiofrequency for the treatment of primary trigeminal neuralgia: a randomized controlled trial.J Neurosurg. 2025 Mar 7;143(1):100-110. doi: 10.3171/2024.10.JNS241274. Print 2025 Jul 1. J Neurosurg. 2025. PMID: 40053922 Clinical Trial.
-
Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical management for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Oct 14;2015(10):CD011165. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011165.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26465274 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Azma T., Nishioka A., Ogawa S., Nagasaka H., Matsumoto N. Enhanced Expression of Gene Coding for β-Endorphin in Human Monocytic Cells Exposed to Pulsed Radio Frequency Electric Fields through Thermal and Non-Thermal Effects. J. Pain Res. 2018;11:2887–2896. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S171974. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

