A Multimodal Physical Program Combining Abacus Use and Exercise to Improve Motor Coordination and Flexibility in Primary School Children
- PMID: 40700191
- PMCID: PMC12285966
- DOI: 10.3390/jfmk10030255
A Multimodal Physical Program Combining Abacus Use and Exercise to Improve Motor Coordination and Flexibility in Primary School Children
Abstract
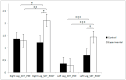
Background: During early childhood, physical development plays a critical role in overall growth, influencing not only health but also academic and social outcomes. In this context, the present randomized controlled trial aims to analyze the effects of a combined intervention using physical exercise and abacus training on flexibility and motor coordination in early primary school children. Methods: A total of 82 girls and boys participated in this study, of which 41 belonged to the experimental group that carried out a combined training of physical exercise and the use of an abacus for 12 weeks and 41 to a control group that did not receive any intervention. Flexibility was measured with the Sit and Reach test and motor coordination with the motor coordination test. Results: In this study, statistically significant improvements were observed in flexibility in both the right and left legs and in all domains related to motor coordination in the training group. Conclusions: The results of this study support the effectiveness of a multidimensional approach that integrates physical and cognitive activities, such as the use of the abacus, to improve coordination and flexibility in children, contributing to comprehensive development in early childhood education.
Keywords: abacus; children; flexibility; motor coordination; physical exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Apr 30;(4):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3:CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. PMID: 23633361 Updated.
-
Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 31;3(3):CD008796. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008796.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27030386 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 24;4(4):CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28436583 Free PMC article.
-
Physical activity and exercise for chronic pain in adults: an overview of Cochrane Reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 14;1(1):CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 24;4:CD011279. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011279.pub3. PMID: 28087891 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Education support services for improving school engagement and academic performance of children and adolescents with a chronic health condition.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 8;2(2):CD011538. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011538.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36752365 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Omenebele-Kaizar V., Ochuko-Alordiah C. Understanding the role of play in promoting cognitive, social, and emotional development in school children: Implications for counsellors and evaluators. J. Contemp. Stud. Educ. 2023;2
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

