Rituximab Therapy in Refractory Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid: A Case Report
- PMID: 40700248
- PMCID: PMC12286205
- DOI: 10.3390/reports8030115
Rituximab Therapy in Refractory Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid: A Case Report
Abstract
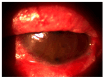
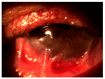
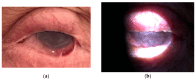
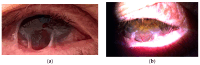
Background and Clinical Significance: Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid (OCP) is a rare autoimmune disease affecting the conjunctiva and oral mucosa. Chronic inflammation causes conjunctival scarring, leading to symblepharon, trichiasis, corneal damage, and possible blindness. Diagnosis is clinical, supported by biopsy and immunofluorescence. Treatment includes systemic corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, and biologics in refractory cases. Case Presentation: A 64-year-old male presented with ocular irritation, trichiasis, and counting fingers (CF) visual acuity in the left eye. Slit-lamp examination revealed conjunctival inflammation, corneal epithelial defect, and symblepharon in the left eye. Biopsy confirmed ocular cicatricial pemphigoid (OCP). He was treated with topical steroids, cyclosporine, subconjunctival injections, and systemic corticosteroids, followed by surgery, which improved BCVA to 0.10 logMAR. Two years later, disease progression resulted in severe inflammation and visual decline in both eyes. Systemic azathioprine and corticosteroids achieved partial control. Due to insufficient response, rituximab therapy was initiated, leading to significant reduction in inflammation and stabilization of disease. Right eye BCVA improved to 0.16 logMAR; the left remained at CF. The patient continues to receive rituximab during exacerbations and is under regular follow-up. Conclusions: Early diagnosis and timely systemic treatment are essential in preventing vision loss in OCP. In refractory cases, biologic agents like rituximab may offer effective disease control.
Keywords: biologic therapy; mucous membrane pemphigoid; ocular cicatricial pemphigoid; rituximab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Scleral Lens Use in the Management of Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid.Eye Contact Lens. 2025 Apr 1;51(4):201-205. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000001172. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Eye Contact Lens. 2025. PMID: 39888633
-
Non-biologic, steroid-sparing therapies for non-infectious intermediate, posterior, and panuveitis in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 31;10(10):CD014831. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014831.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36315029 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges and advances in ocular mucous membrane pemphigoid (OMMP); from pathogenesis to treatment strategies.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025 Jun;263(6):1489-1502. doi: 10.1007/s00417-025-06756-2. Epub 2025 Feb 5. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39909902 Review.
-
Amniotic membrane transplantation for acute ocular burns.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 1;9(9):CD009379. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009379.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36047788 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Relapsing Hailey-Hailey Disease Displaying a Durable Complete Response to Hydroxyurea.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024 Nov;32(3):168-169. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2024. PMID: 40654217
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources