Impact of Light-Chain Variants on the Expression of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies in HEK293 and CHO Cells
- PMID: 40700293
- PMCID: PMC12286288
- DOI: 10.3390/antib14030053
Impact of Light-Chain Variants on the Expression of Therapeutic Monoclonal Antibodies in HEK293 and CHO Cells
Abstract
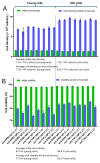
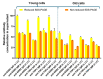
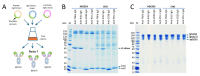
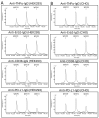
Recombinantly produced monoclonal antibodies (mabs) belong to the fastest growing class of biotherapeutics. In humans, antibodies are classified into five different classes: IgA, IgD, IgE, IgG and IgM. Most of the therapeutic mabs used in the clinic belong to the IgG class, albeit other antibody classes, e.g., IgM, have been evaluated in clinical stages. Antibodies are composed of heavy chains paired with a light chain. In IgM and IgA, an additional chain, the J-chain, is present. Two types of light chains exist in humans: the κ-light chain and the λ-light chain. The κ-light chain predominates in humans and is used in the vast majority of therapeutic IgG. The reason for the preference of the κ-light chain in humans is not known. Our study investigates whether light-chain selection influences the productivity of the clinically validated mabs adalimumab and trastuzumab. Both mabs were expressed as IgG and IgM with a κ- or a λ-light chain in HEK293 cells. Besides comparing the expression levels of the different mabs, we also evaluated whether the passage number of the cell line has an impact on product yield. In addition, the expressions of adalimumab, trastuzumab, an anti-CD38 and an anti-PD-L1-antibody were analyzed in HEK293 and CHO cells when both the κ- and λ-light chains are present. In summary, IgG outperformed IgM variants in expression efficacy, while light-chain selection had minimal impact on the overall expression levels. The yields of all mab variants were higher in fresh cells, despite cell cultures with a high cell passage number having higher cell densities and cell numbers at the time of harvest. The incorporation of a particular light chain occurred at similar rates in HEK293 and CHO cells.
Keywords: CHO cells; HEK cells; Immunoglobulin G (IgG); Immunoglobulin M (IgM); Kappa and Lambda light chain; recombinant expression.
Conflict of interest statement
A.V., D.L., P.G., D.K.B., I.F., W.D.L., C.B., S.W., E.R. and T.L. are employees of Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH and may hold company shares and/or stock options. A.V. was, during the time of the study, a registered student at Provadis School of International Management and Technology AG, Frankfurt am Main, and working at Sanofi-Aventis Deutschland GmbH. However, the authors declare no additional conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Strohl W.R., Strohl L.M. Therapeutic Antibody Engineering. Woodhead Publishing; Sawston, UK: 2012. pp. 111–129, 459–595. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

