Radiomics analysis for the early diagnosis of common sexually transmitted infections and skin lesions
- PMID: 40700364
- PMCID: PMC12286352
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pdig.0000926
Radiomics analysis for the early diagnosis of common sexually transmitted infections and skin lesions
Abstract
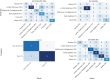
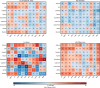
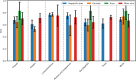
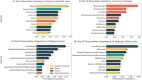
Early identification of sexually transmitted infection (STI) symptoms can prevent subsequent complications and improve STI control. We analysed 597 images from STIAtlas and categorised the images into four typical STIs and two skin lesions by the anatomical sites of infections. We first applied nine image filters and 11 machine-learning image classifiers to the images. We then extracted radiomics features from the filtered images and trained them with 99 models that combined image filters and classifiers. Model performance was evaluated by area under curve (AUC) and permutation importance. When the information of infection sites was unspecified, a combined Gradient-Boosted Decision Trees (GBDT) classifier and Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filter model achieved the best overall performance with an average AUC of 0.681 (95% CI 0.628-0.734). This model predicted best for lichen sclerosus (AUC = 0.768, 0.740-0.796). The incorporation of infection site information led to a substantial improvement in the model's performance, with 22.3% improvement for anal infections (AUC = 0.833, 0.687-0.979) and 3.8% for skin infections (AUC = 0.707, 0.608-0.806). Lesion texture and statistical radiomics features were the most predictive for STIs. Combining machine learning and radiomics techniques is an effective method to categorise skin lesions associated with STIs clinically.
Copyright: © 2025 Sun et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Are Current Survival Prediction Tools Useful When Treating Subsequent Skeletal-related Events From Bone Metastases?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Sep 1;482(9):1710-1721. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003030. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38517402
-
Population-based biomedical sexually transmitted infection control interventions for reducing HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21412869
-
Comparison of Two Modern Survival Prediction Tools, SORG-MLA and METSSS, in Patients With Symptomatic Long-bone Metastases Who Underwent Local Treatment With Surgery Followed by Radiotherapy and With Radiotherapy Alone.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Dec 1;482(12):2193-2208. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003185. Epub 2024 Jul 23. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 39051924
-
Machine learning models for discriminating clinically significant from clinically insignificant prostate cancer using bi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging.Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025 Jul 8;31(4):313-320. doi: 10.4274/dir.2024.242856. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39354727 Free PMC article.
-
Population-based interventions for reducing sexually transmitted infections, including HIV infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(2):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Mar 16;(3):CD001220. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001220.pub3. PMID: 15106156 Updated.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) [cited 2023 1 December]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/sexually-transmitted-in...
-
- Du M, Yan W, Jing W, Qin C, Liu Q, Liu M, et al. Increasing incidence rates of sexually transmitted infections from 2010 to 2019: an analysis of temporal trends by geographical regions and age groups from the 2019 Global Burden of Disease Study. BMC Infect Dis. 2022;22(1):574. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07544-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO. Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections. World Health Organization; 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
