An ICEEMDAN and SAX-based method for determining English reading comprehension status using functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals
- PMID: 40700404
- PMCID: PMC12286323
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0326359
An ICEEMDAN and SAX-based method for determining English reading comprehension status using functional near-infrared spectroscopy signals
Abstract
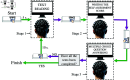
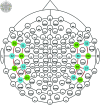
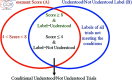
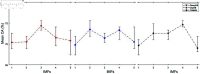
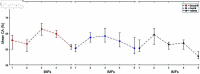
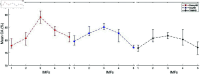
Accurate, rapid, and objective reading comprehension assessments, which are critical in both daily and educational lives, can be effectively conducted using brain signals. In this study, we proposed an improved complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (ICEEMDAN) and symbolic aggregate approximation (SAX)-based method for determining the whole text reading comprehension status in English using functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) signals. A total of 450 trials were recorded from 15 healthy participants as they read English texts. To facilitate labeling, participants were asked to rate their comprehension of the text using self-assessment scores, followed by answering a multiple-choice question with four options that comprehensively covered the whole text's content. The proposed method consists of pre-processing, feature extraction, and classification stages. In the pre-processing stage, intrinsic mode functions of the signals were obtained using the ICEEMDAN algorithm. In the feature extraction stage, following the SAX algorithm, statistical features were calculated. The extracted features were classified using the k-NN classifier. The proposed method tested three different labeling strategies: first, labeling the trials according to the responses to multiple-choice questions; second, labeling the trials based on self-assessment scores; and third, labeling the trials using a double-validation labeling strategy based on the intersection sets of the first two strategies. For the three strategies, the k-NN classifier achieved mean classification accuracies of 74.67%, 66.37%, and 89.02%, respectively. The results indicated that the proposed method could assess whole-text reading comprehension status in English.
Copyright: © 2025 Akincioglu et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures








References
-
- Kintsch W, van Dijk TA. Toward a model of text comprehension and production. Psychol Rev. 1978;85(5):363–94. doi: 10.1037/0033-295x.85.5.363 - DOI
-
- Snow CE. Reading for understanding: toward an R&D program in reading comprehension. RAND Corporation; 2002.
-
- Yuan Y, et al. Toward unobtrusive measurement of reading comprehension using low-cost EEG. In: LAK ’14: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Learning Analytics and Knowledge, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA. 2014. p. 54–8.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

