Novel potential of low calorie plant burger: Functional turkey meat formulation optimized by replacing quinoa, chia, soy, amaranth and peas as vegetable protein and their influence on texture and sensory traits
- PMID: 40700423
- PMCID: PMC12286408
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325622
Novel potential of low calorie plant burger: Functional turkey meat formulation optimized by replacing quinoa, chia, soy, amaranth and peas as vegetable protein and their influence on texture and sensory traits
Abstract
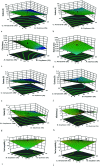
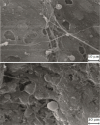
This study explores the creation of a nutritionally and low-calorie turkey burger by integrating plant-based protein concentrates. Turkey burgers formulated with quinoa, chia, soybean, amaranth and pea proteins at inclusion levels of 0 and 30%. A Taguchi L8 orthogonal array employed to evaluate the effects on water (WHC) and oil (OHC) holding capacities, cooking loss, chemical properties, emulsion activity and stability. Optimal formulations including quinoa, soybean and amaranth at levels of 0, 12.5 and 25% developed using response surface methodology with a central composite design, emphasizing texture and overall acceptability and also microstructure analyzed through scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The glutamic acid identified as the most abundant amino acid across all protein types. The burgers made entirely of turkey meat displayed the lowest pH (6.13) and protein content (17.36%). In contrast, the meat free samples exhibited higher moisture, fat, ash and fiber content along with improved WHC and also OHC and reduced cooking loss. Plant protein formulations showed enhanced elasticity and lower levels of hardness, cohesiveness and chewiness compared to the meat-only samples. Sensory evaluations indicated an inclusion preference for protein concentrates with the optimal formulation consisting of 25% quinoa, 11.86% soybean, and 25% amaranth. SEM analysis confirmed the successful integration of vegetable proteins into the burger matrix. These findings highlighted the potential for mass-producing turkey burgers with reduced meat content, enhanced nutritional value, functional and sensory properties.
Copyright: © 2025 Erfanian, Nouri. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Bundur A, Riaz R, Elibol FKE, Demir T, Polo J, Crenshaw J, et al. Effects of spray-dried plasma on performance, carcass parameters, tibia quality and Newcastle disease vaccine efficacy in broiler chicken fed corn-soy diets with two varying levels of digestible amino acids and AMEn density. PLoS One. 2024;19(9):e0309263. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309263 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vu G, Zhou H, McClements DJ. Impact of cooking method on properties of beef and plant-based burgers: Appearance, texture, thermal properties, and shrinkage. Journal of Agriculture and Food Research. 2022;9:100355. doi: 10.1016/j.jafr.2022.100355 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

