Assessing the risk of diseases with epidemic and pandemic potential in a changing world
- PMID: 40700491
- PMCID: PMC12285694
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adw6363
Assessing the risk of diseases with epidemic and pandemic potential in a changing world
Abstract
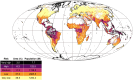
How do human activities contribute to the emergence of zoonotic diseases that can lead to epidemics and pandemics? Our analysis of common drivers of the World Health Organization's priority diseases suggests that climate conditions, including higher temperatures, higher annual precipitation levels, and water deficits, elevate the risk of disease outbreaks. In addition, land-use changes, human encroachment on forested areas, increased population and livestock density, and biodiversity loss contribute to this risk, with biodiversity loss showing a complex and nonlinear relationship. This study also presents a global risk map and an epidemic risk index that combines countries' specific risk with their capacities for preparing and responding to zoonotic threats.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Measures implemented in the school setting to contain the COVID-19 pandemic.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 17;1(1):CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 May 2;5:CD015029. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015029.pub2. PMID: 35037252 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Effects of global change drivers on the expression of pathogenicity and stress genes in dryland soil fungi.mSphere. 2024 Nov 21;9(11):e0065824. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00658-24. Epub 2024 Oct 30. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39475318 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Temperature on the Distribution of Zoonotic Pathogens in Livestock and Wildlife Populations: A Systematic Review.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023 Aug 18;2023:2714539. doi: 10.1155/2023/2714539. eCollection 2023. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023. PMID: 40303667 Free PMC article.
-
Synergies Between Agricultural Production and Shorebird Conservation With Climate Change in the Central Valley, California, With Optimized Water Allocation and Multi-Benefit Land Use.Glob Chang Biol. 2025 Jun;31(6):e70304. doi: 10.1111/gcb.70304. Glob Chang Biol. 2025. PMID: 40539289 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the research gap of zoonotic disease in displacement: a systematic review.Glob Health Res Policy. 2021 Jul 16;6(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s41256-021-00205-3. Glob Health Res Policy. 2021. PMID: 34271977 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

